Adaptive Facades
Adaptive Façades
An Integrated Algorithmic Approach
Helena Luísa Freitas Martinho
Thesis to obtain the Master of Science Degree in
Architecture
Instituto Superior Técnico, May 2019

The concept of architectural performance comprises an understanding of the interaction between the built and natural environments. Over the past decades, design practices started envisioning the future of façade conception through the use of environmentally reactive components.

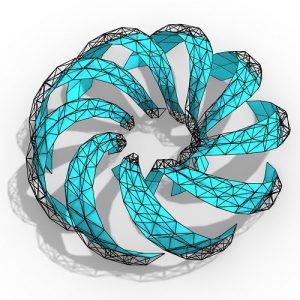
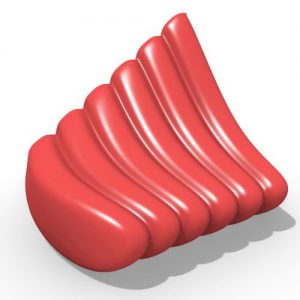
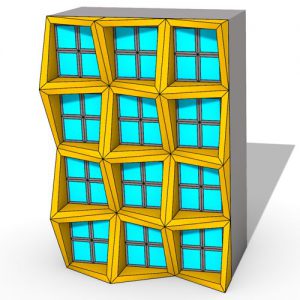
Covering solutions that vary in terms of materials, components, and systems, adaptive façades provide new aesthetic opportunities by offering the potential to reduce energy demands while enhancing the indoor comfort.

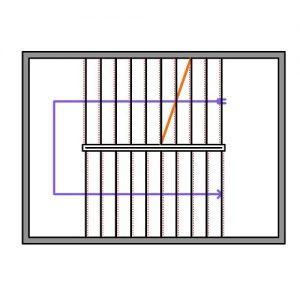
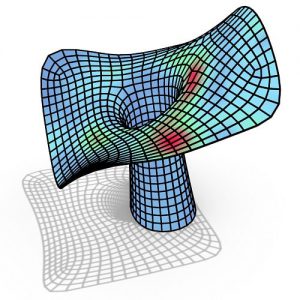
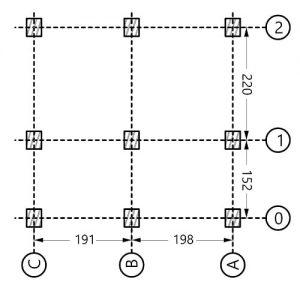
However, as traditional simulation tools target the design of static geometries, and adaptive façades encompass an envisioned movement of construction elements, there is a lack of supporting tools and workflows that can correctly evaluate the performance of these systems at an early design stage.

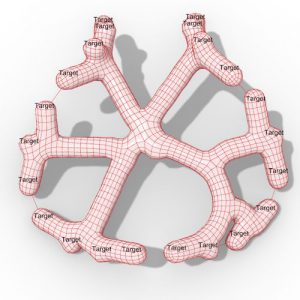
On the other hand, there is a growing potential in Algorithmic Design (AD) strategies, which remains largely unexplored in the architectural context, regarding both early design stages and the modeling of adaptive façades.

The presented research by Helena Luísa Freitas Martinho aims to develop a unified AD and analysis workflow for the energy performance assessment of adaptive façades. The goal is to further reduce the current gap between form- finding and analytical tasks during project conception, through the adoption of a performance-based design approach.

Author shows that the goal is attainable by integrating the generation of parametric models and the execution of energy simulations into a single algorithmic description, evaluating and using the simulation results to develop optimized control strategies.











Comments