Deployable Tensegrity Structures
DEPLOYABLE TENSEGRITY STRUCTURES USING PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION MEMBERS
Jonathan DESSI-OLIVE1, James CASE2, Michael KOLINER1, Vinay TEJA MEDA2, and Chris PUTMAN2
1School of Architecture, Georgia Institute of Technology 245 4th Street NW, Atlanta, GA
2Uzun + Case, Structural Engineering 1230 Peachtree Street, NE, Suite 2500, Atlanta, GA

Figure 1: A proof-of-concept prototype for deployable inflatable tensegrity structure.
A hybridized structure system is introduced, which extends the principles of active-deployed tensegrity structures through a series of prototypes that use pneumatic compression struts, resulting in a minimum weight deployable structure with maximal global volume change.
The design and construction of the prototypes, analytical strategies for the performance of such air-struts under compression, and speculation on material possibilities, and the applications of pneumatic tensegrity structures will be discussed.
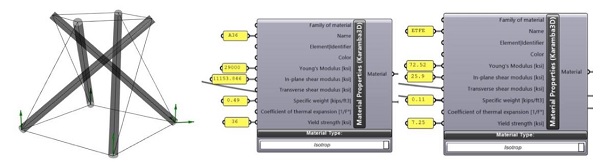
Figure 2. Basic 4-strut Tensegrity
Figure 3. Input parameters for cables and struts.
Tensegrity structures are considered to be optimal because they maintain their stability with the fewest possible number of structural members carrying purely axial forces.
Since their introduction in the mid-twentieth century, artists, architects, and engineers have imagined applications for tensegrity structures and several innovative variations to the system have been proposed.

Figure 6. End-cap and valve detail with tension cables. Shown with 2 layers of HDPE tubing.
This paper presents advancements in a hybridized structure system that extends the principles of active-deployed tensegrity structures through a series of physical prototypes that use pneumatic compression struts.
Replacing rigid compression struts traditionally found in tensegrity structures with pneumatic members presents an opportunity to maximize the global volume change of the structure before and after it is deployed, and minimize its overall weight.

Figure 7. Three-Strut Prototype.
Figure 8. Four-strut Prototype.
Though proven to be theoretically possible, no large-scale physical prototypes have been developed. The research presented in this paper is focused on developing preliminary construction strategies for architectural-scale deployable tensegrity structures that use low-pressure air-struts.
Due to the unique combination of two historic structural systems, this paper will first review the origins, historical context, and applications of pneumatic and tensegrity structures in arch`itecture and give an overview of previous proposals of inflatable tensegrity systems in other fields.

Figure 9. Cable-Reinforced Air-Strut Prototype.
Next, theoretical, analytical and design strategies for this hybrid structure system will be described, followed by a discussion of a series of physical inflatable tensegrity prototypes at increasing scale and technological resolution.
Finally, this paper will specify next steps in development of large-scale inflatable tensegrity structures, and speculate on the range of material possibilities and applications such structures may have.










Comments