String Art Generator
String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can


Addressing both architects and engineers, this dissertation by Matthias Rippmann presents a new framework for the form finding and design of fabrication geometry of discrete, funicular structures in the early design phase. Motivated by ongoing debates about digital architecture and funicular shell form finding, it introduces a new methodology for structurally-informed design of curved surface architecture through the use of geometrical rather than analytical or numerical representations of the relation between form, forces and fabrication.

Based on Thrust Network Analysis (TNA), new algorithms are presented that enable an interactive exploration of novel funicular shapes, enriching the known formal vocabulary of shell architecture. Using TNA, the framework adopts the same advantages of techniques like graphic statics, providing an intuitive and educational approach to structural design that ranges from simple explorations to geometry-based optimization techniques.

Complementary to this structurally informed design process, the work reflects on the latest building technologies while also revisiting historic construction techniques for stereotomic stone masonry and prefabricated concrete shells to develop efficient fabrication design strategies for discrete funicular structures. Based on architectural, structural and fabrication requirements, several tessellation approaches for given thrust surfaces are developed for the design of informed discretisation layouts of any funicular shape.
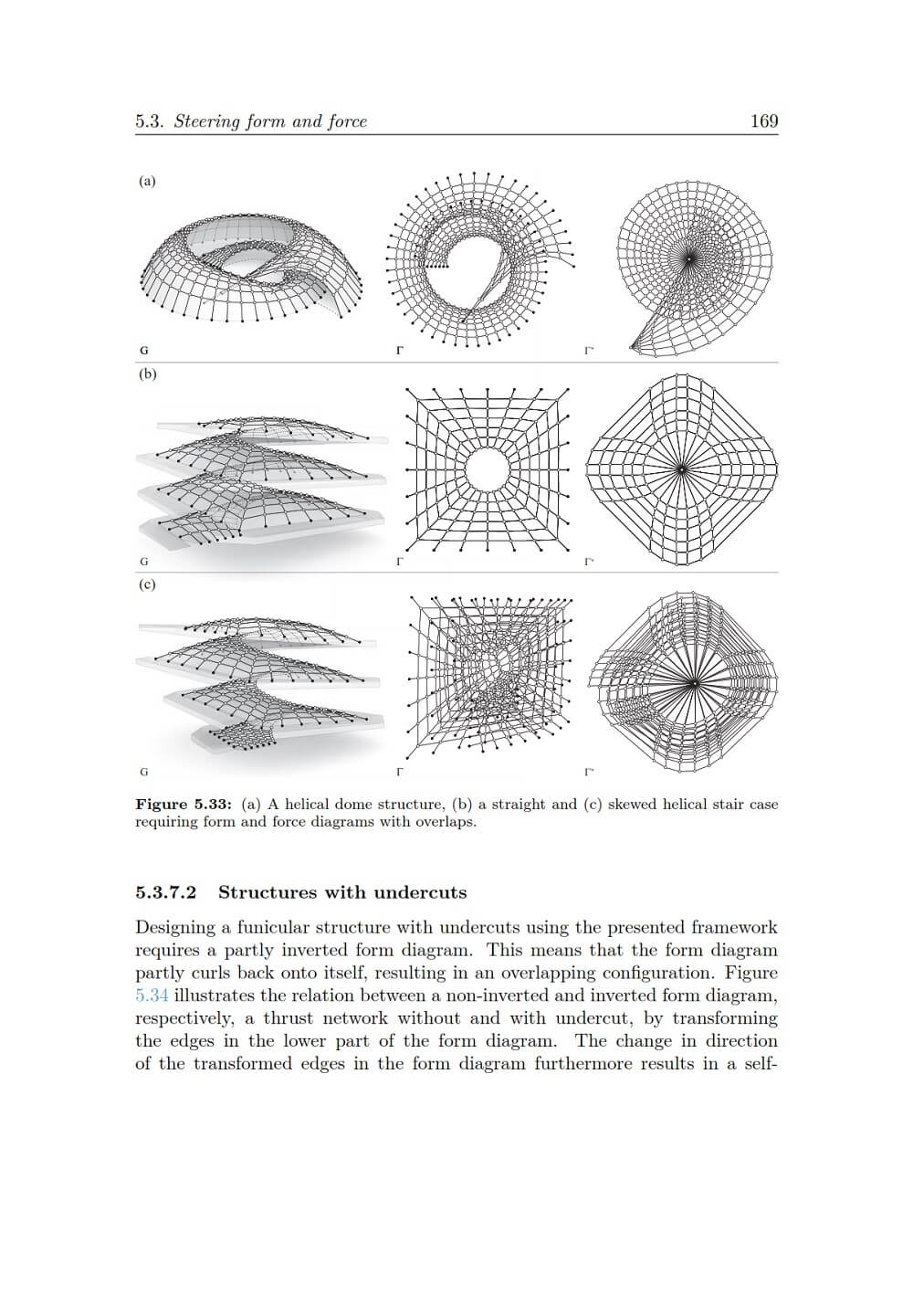
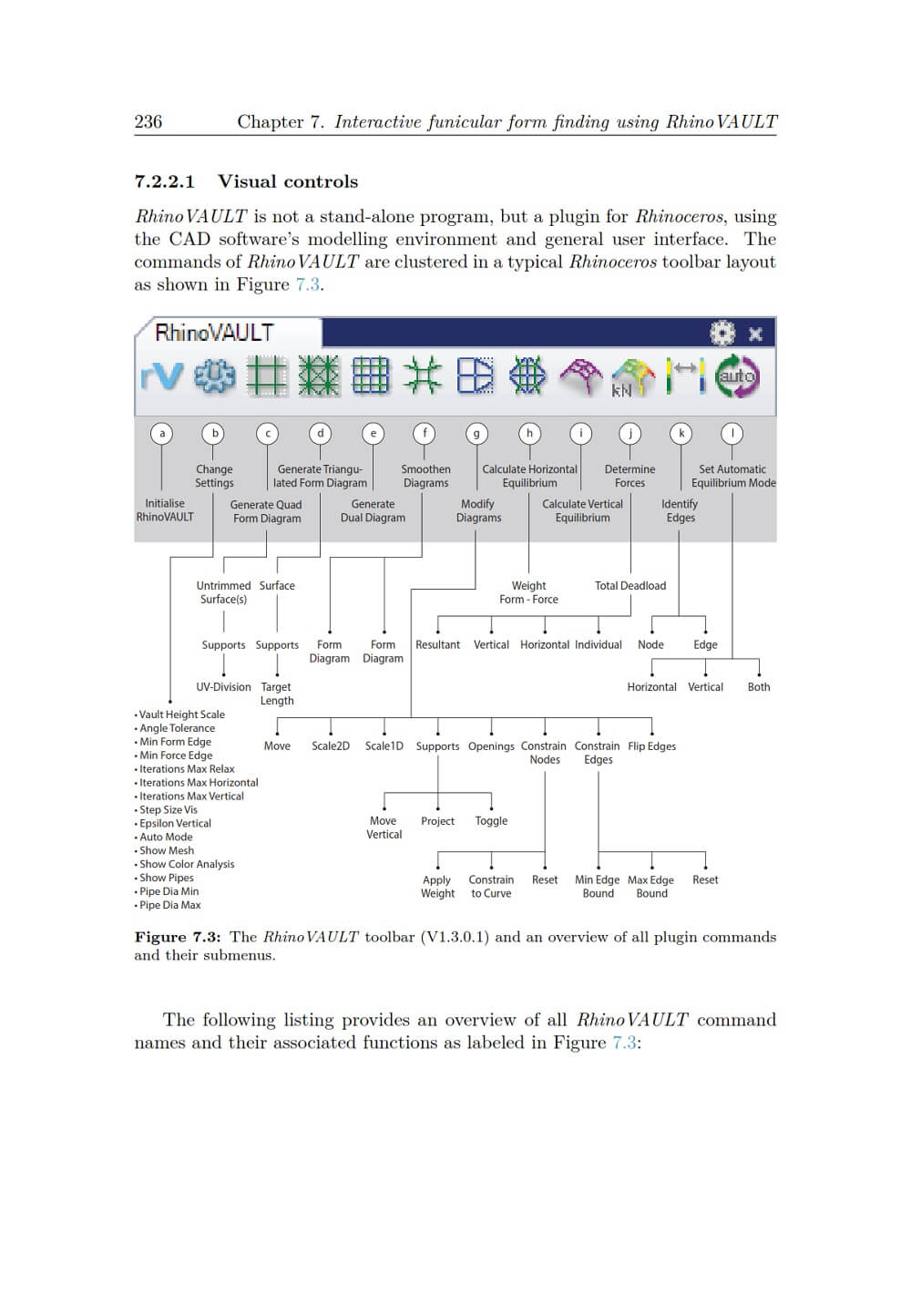
The flexibility and feasibility of the form-finding framework is demonstrated in several case studies employing the new structural design tool RhinoVAULT, which implements the developed form-finding methods. The use of fabrication design strategies is discussed in a comprehensive case study that shows project-specific tessellation design variations and first fabrication results for a complex stone masonry shell.





String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can

This paper by Alessandro Liuti, Sofia Colabella, and Alberto Pugnale, presents the construction of Airshell, a small timber gridshell prototype erected by employing a pneumatic formwork.

In this paper by Gregory Charles Quinn, Chris J K Williams, and Christoph Gengnagel, a detailed comparison is carried out between established as well as novel erection methods for strained grid shells by means of FE simulations and a 3D-scanned scaled physical model in order to evaluate key performance criteria such as bending stresses during erection and the distance between shell nodes and their spatial target geometry.

In this paper by Frederic Tayeb, Olivier Baverel, Jean-François Caron, Lionel du Peloux, ductility aspects of a light-weight composite gridshell are developed.
Parametric Ideas for Architects @2025