Interactive Facade
Interactive Facade
Tella Irani Shemirani
A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master in Architecture
Carleton University Ottawa, Ontario
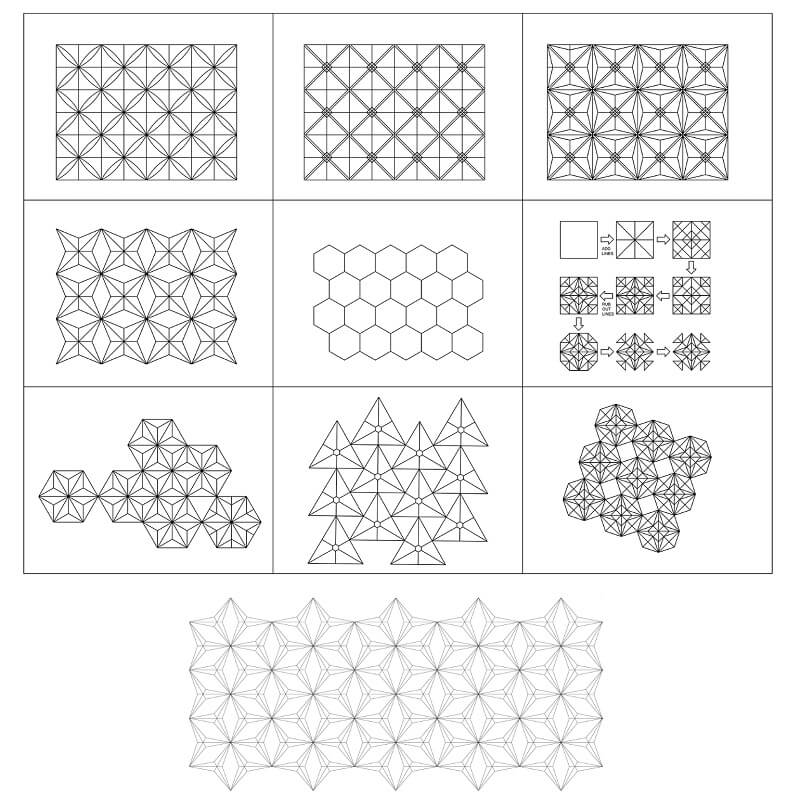
Today, new digital technologies can play an important role in accelerating information processing, leading to new communication technologies. At the same time, digital technology is rapidly increasing the dynamic interaction between building and users.

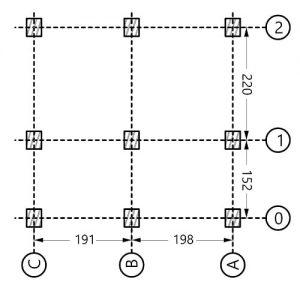
The overlap of digital technology with the field of architecture has resulted in the development of Interactive Architecture, architecture that evolve beyond parametric and generative design, incorporating new technological advances, absorbing, processing and exchanging data in real time, proposing configuration adapted to the ever-changing needs of its users.
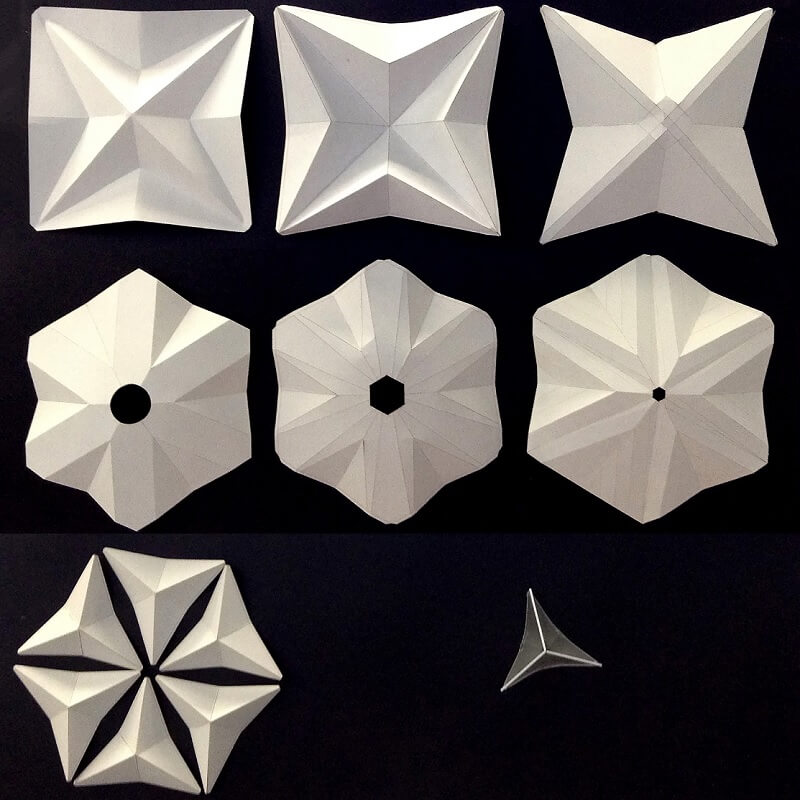
For instance, new computing technologies are developing an intelligent architecture, allowing buildings to sense and analyze their surroundings, and make decisions to evolve an appropriate response to environmental stimuli through adaptation. Interactive Architecture designs space capable of communicating and interacting with the changing.

This thesis by Tella Irani Shemirani is focused on investigating the question of: How can a space develop an understanding of its users (through their body gestures) and respond accordingly? Based on the thesis question this paper investigates the process of creating interactive spaces and explores architectural form generation through behaviour-based AI approaches. The thesis concludes with a proposal for a dynamic responsive architectural system, a through behaviour-based AI approaches.
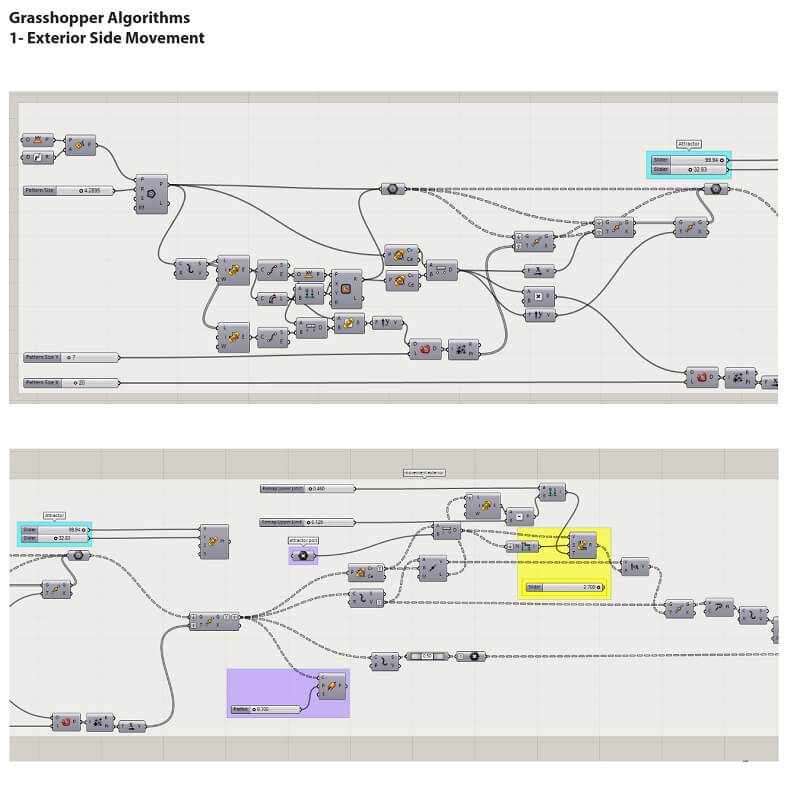
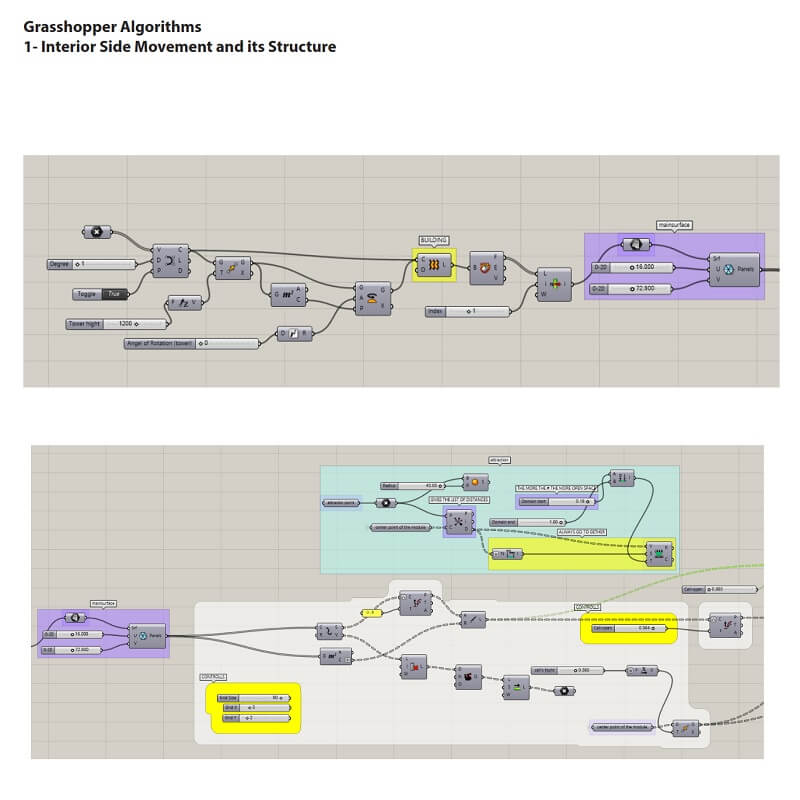
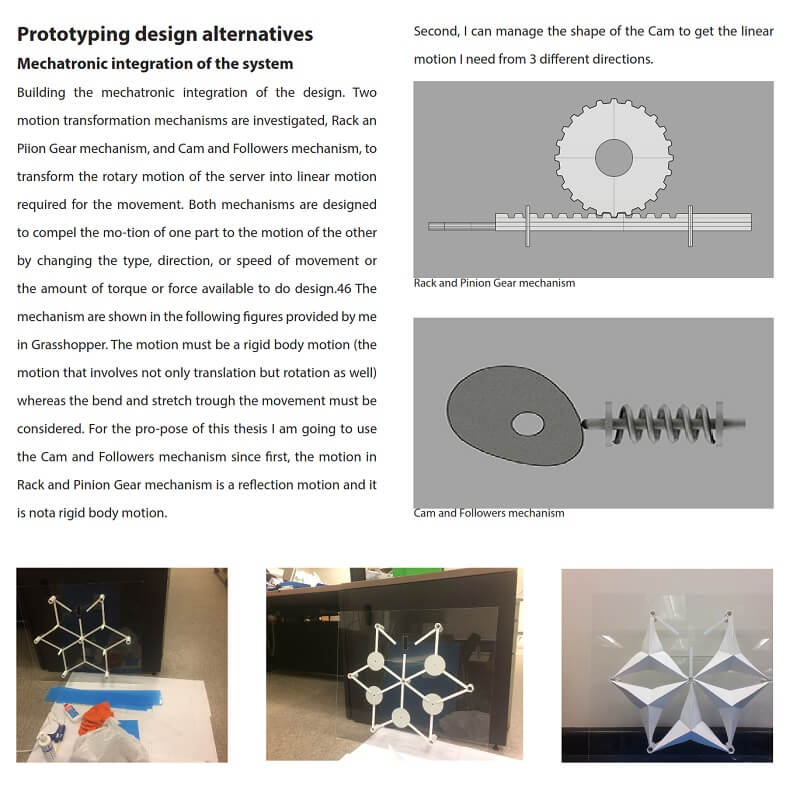
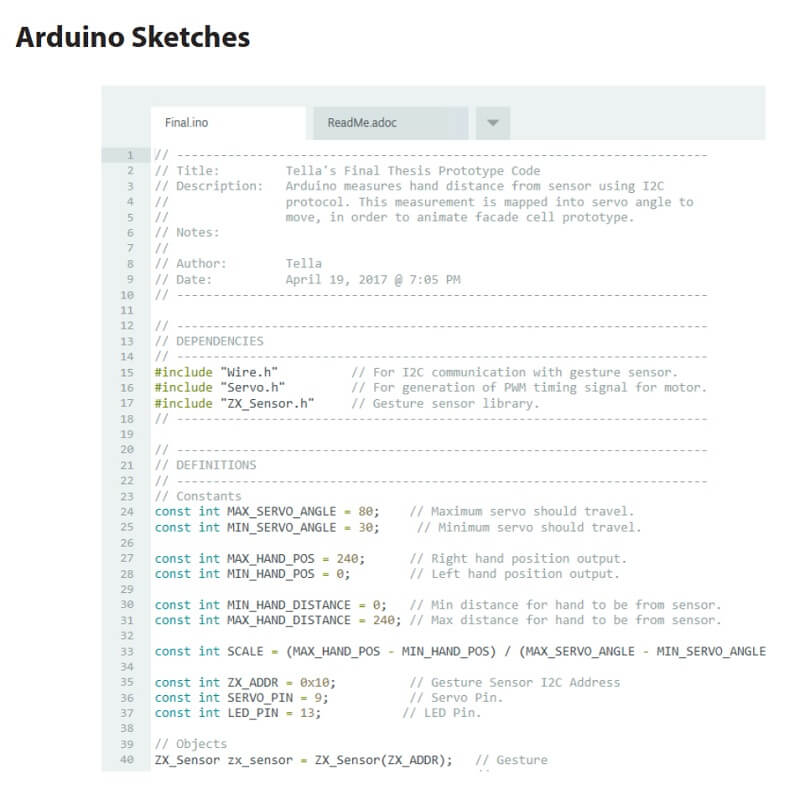











Comments