String Art Generator
String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can

 Architects used to be the chief builder that controls the whole design process starting from early design phases till the final end-product construction. By the time specialization and the use of mass-produced building components spread widely and dominate all industrial fields and architects became more separated from many key aspects of a building’s production. New technologies, including digital generative design and digital fabrication systems can narrow the gap between architectural designs, associative engineering aspects and buildings construction and reintegrate them into a digitally collaborative cycle process where architects is the “chief builder” again. In this regard, parametric generative systems as well as optimization algorithms, have made a major shift in the design process from designing an ‘object’ to design the ‘logic’ of the object, considering parametric optimization approach as a generative-explorative tool.
Architects used to be the chief builder that controls the whole design process starting from early design phases till the final end-product construction. By the time specialization and the use of mass-produced building components spread widely and dominate all industrial fields and architects became more separated from many key aspects of a building’s production. New technologies, including digital generative design and digital fabrication systems can narrow the gap between architectural designs, associative engineering aspects and buildings construction and reintegrate them into a digitally collaborative cycle process where architects is the “chief builder” again. In this regard, parametric generative systems as well as optimization algorithms, have made a major shift in the design process from designing an ‘object’ to design the ‘logic’ of the object, considering parametric optimization approach as a generative-explorative tool.
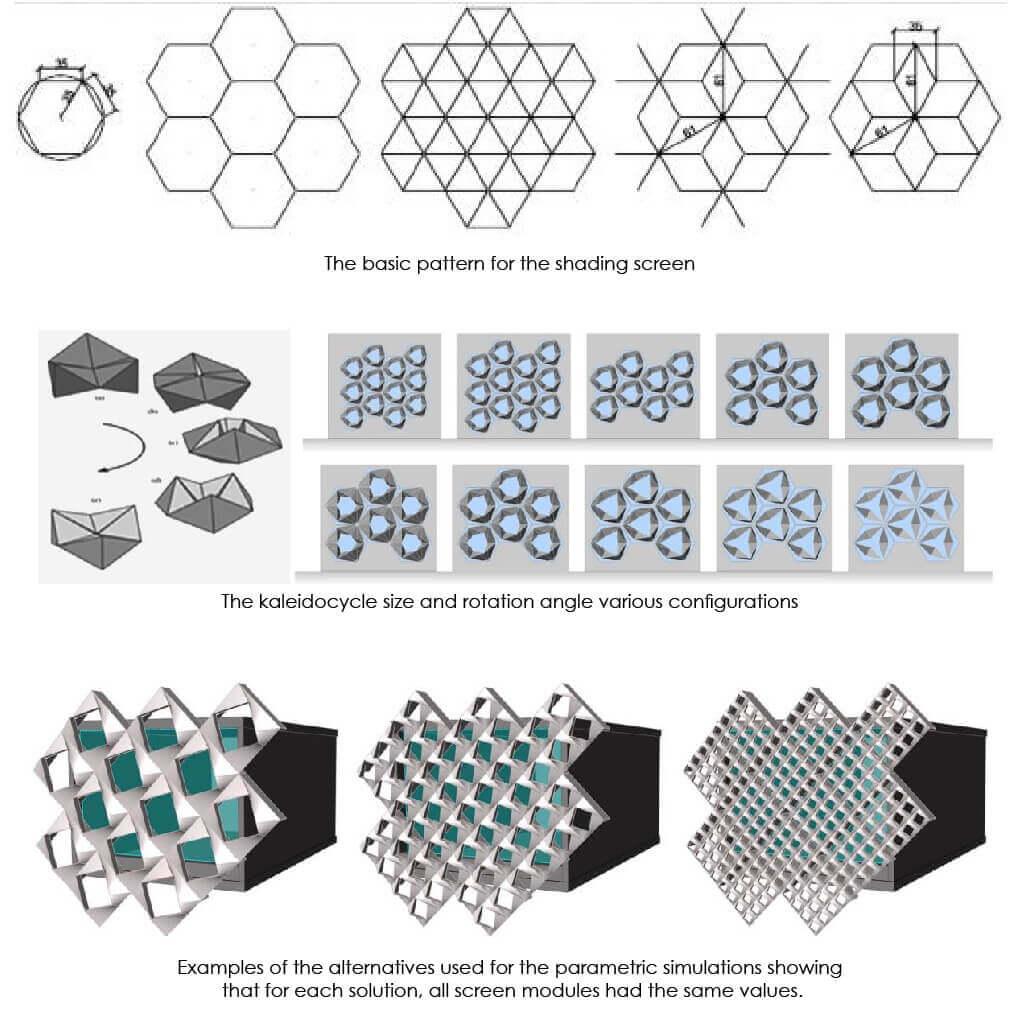
 On the other, hand building façade plays a significant role in architecture; it is not only a mean to express the design concepts but it is the main moderator between interior spaces and exterior environment. The increasing reliance of office buildings on air conditioning and artificial lighting systems indicates the failing role of the building facade to perform its function as a moderator. Within this context, ecological facades have proved their potentials for enhancing buildings’ environmental performance.
On the other, hand building façade plays a significant role in architecture; it is not only a mean to express the design concepts but it is the main moderator between interior spaces and exterior environment. The increasing reliance of office buildings on air conditioning and artificial lighting systems indicates the failing role of the building facade to perform its function as a moderator. Within this context, ecological facades have proved their potentials for enhancing buildings’ environmental performance.
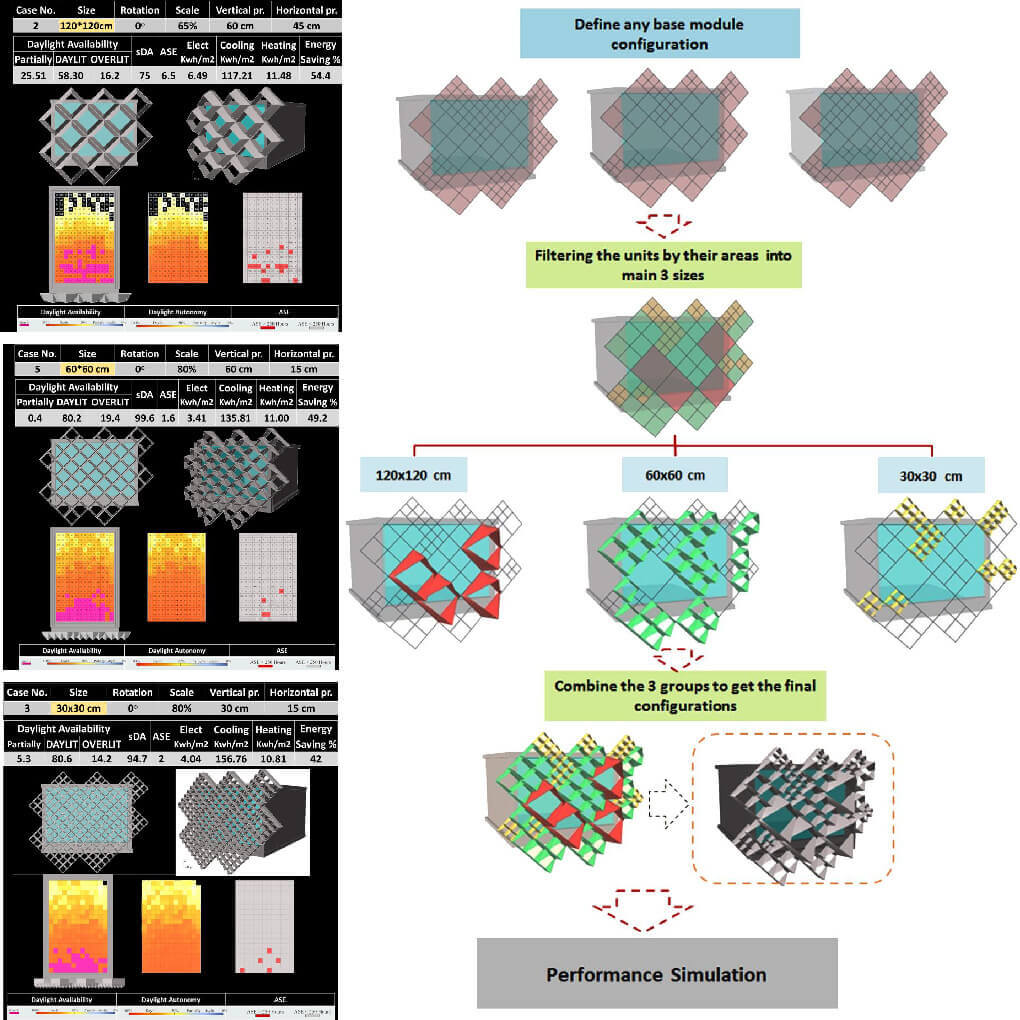
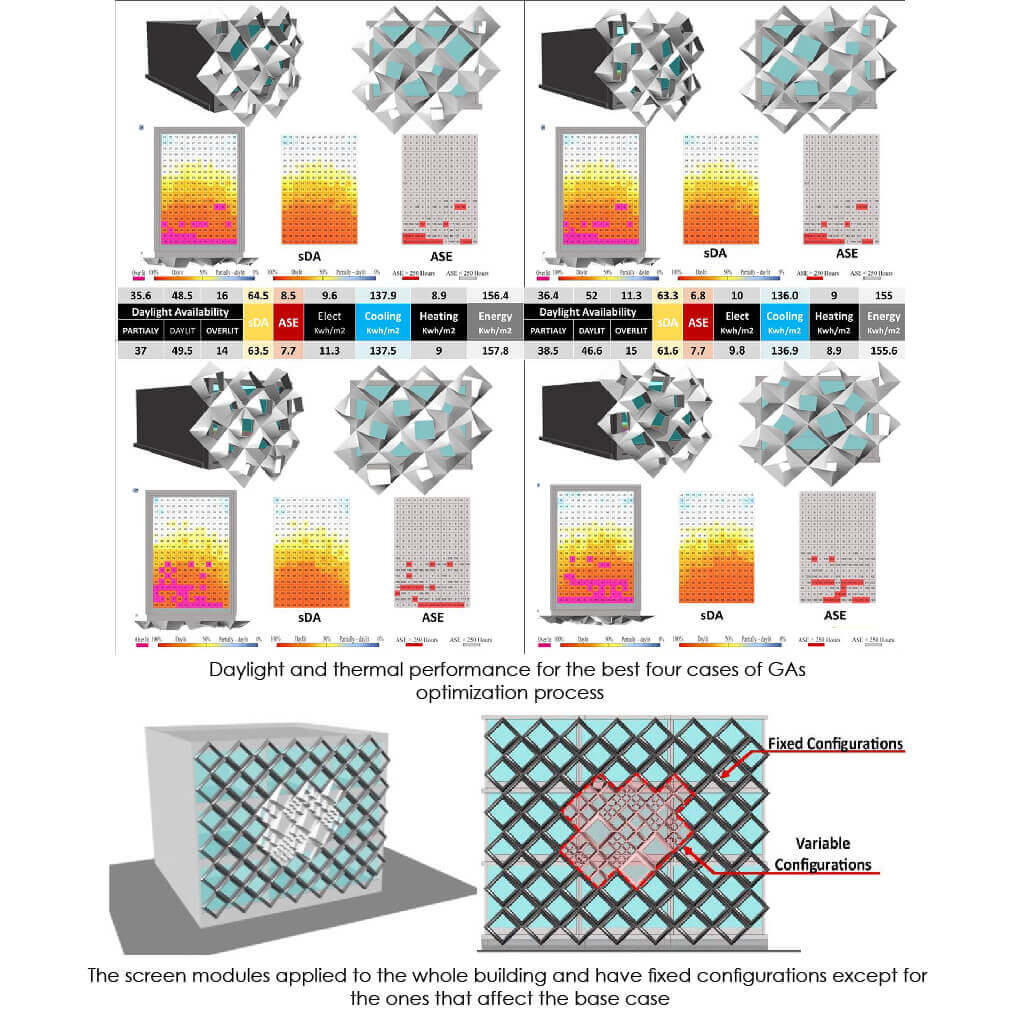 The thesis presented a comprehensive analysis for the effect of the proposed solar screen different parameters on both daylight and thermal performance for office buildings. It addressed evaluation criteria that could give an indication about cooling loads based on daylight simulation and hence daylighting optimum cases can be sorted regarding thermal and energy performance without calculating them. This research also conducted an analytical comparison between the GAs optimization and parametric simulation approach testing each approach’s effectiveness and limitations in balancing daylight and thermal performance for the proposed solar screen. Finally, two parametric-based optimization method; Modified GAs and Adapted Parametric Algorithm, were suggested to overcome the previous limitations. They could help architects to efficiently optimize any non-conventional solar screen regarding specific performance target.
The thesis presented a comprehensive analysis for the effect of the proposed solar screen different parameters on both daylight and thermal performance for office buildings. It addressed evaluation criteria that could give an indication about cooling loads based on daylight simulation and hence daylighting optimum cases can be sorted regarding thermal and energy performance without calculating them. This research also conducted an analytical comparison between the GAs optimization and parametric simulation approach testing each approach’s effectiveness and limitations in balancing daylight and thermal performance for the proposed solar screen. Finally, two parametric-based optimization method; Modified GAs and Adapted Parametric Algorithm, were suggested to overcome the previous limitations. They could help architects to efficiently optimize any non-conventional solar screen regarding specific performance target.

String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can

This paper by Alessandro Liuti, Sofia Colabella, and Alberto Pugnale, presents the construction of Airshell, a small timber gridshell prototype erected by employing a pneumatic formwork.

In this paper by Gregory Charles Quinn, Chris J K Williams, and Christoph Gengnagel, a detailed comparison is carried out between established as well as novel erection methods for strained grid shells by means of FE simulations and a 3D-scanned scaled physical model in order to evaluate key performance criteria such as bending stresses during erection and the distance between shell nodes and their spatial target geometry.

In this paper by Frederic Tayeb, Olivier Baverel, Jean-François Caron, Lionel du Peloux, ductility aspects of a light-weight composite gridshell are developed.
Parametric Ideas for Architects @2025