Timber Reciprocal Frame
Timber reciprocal frame structures
Godthelp, T.S.
Eindhoven University of Technology
The definition ‘Reciprocal Frame’ (RF) applies to structures that are feasible by means of circulating compression or tension interactions between their constituent members.
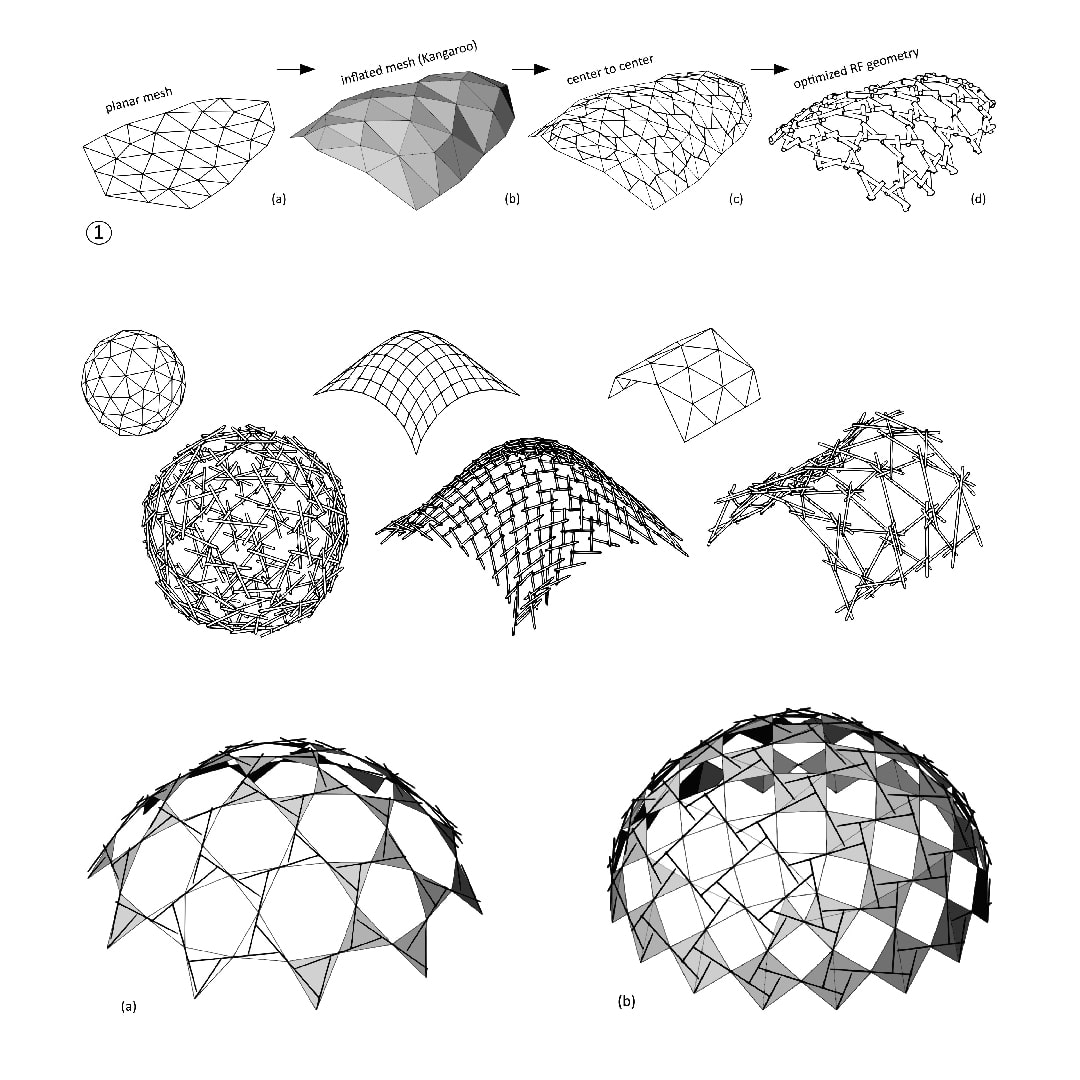
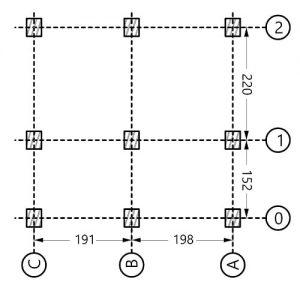
 This relation indicates that beam depths and connections correlate to an RFs’ structural geometry. Until now, a combination of RF form finding that regards both beam depths and structural design of connections has not yet been developed.
This relation indicates that beam depths and connections correlate to an RFs’ structural geometry. Until now, a combination of RF form finding that regards both beam depths and structural design of connections has not yet been developed.
 The goal of this research is to develop a computational design to production tool for vaulted timber reciprocal frame structures using an optimized connection typology and a sustainable timber-based material.
The goal of this research is to develop a computational design to production tool for vaulted timber reciprocal frame structures using an optimized connection typology and a sustainable timber-based material.
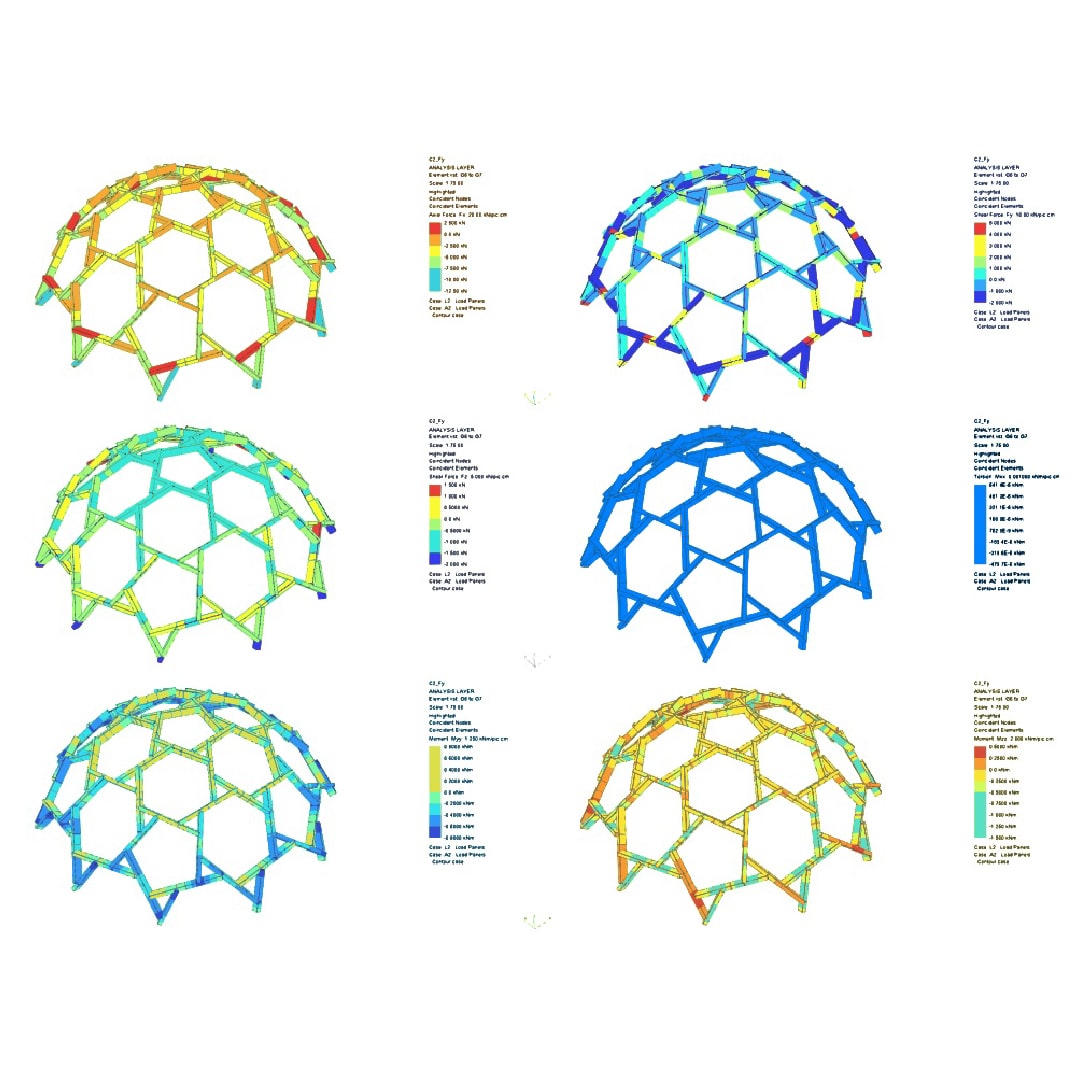
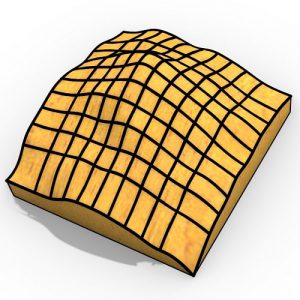
 A geometrical shape is supplemented in the RFD with standardized detailing and beam dimensions that are checked, and if necessary adjusted to satisfy stress and deformation regulations.
A geometrical shape is supplemented in the RFD with standardized detailing and beam dimensions that are checked, and if necessary adjusted to satisfy stress and deformation regulations.
 In conclusion, the RFD provides a tool in which designs can be produced by using industry standard machines stimulating structural designers to add RFs to their design pallet.
In conclusion, the RFD provides a tool in which designs can be produced by using industry standard machines stimulating structural designers to add RFs to their design pallet.
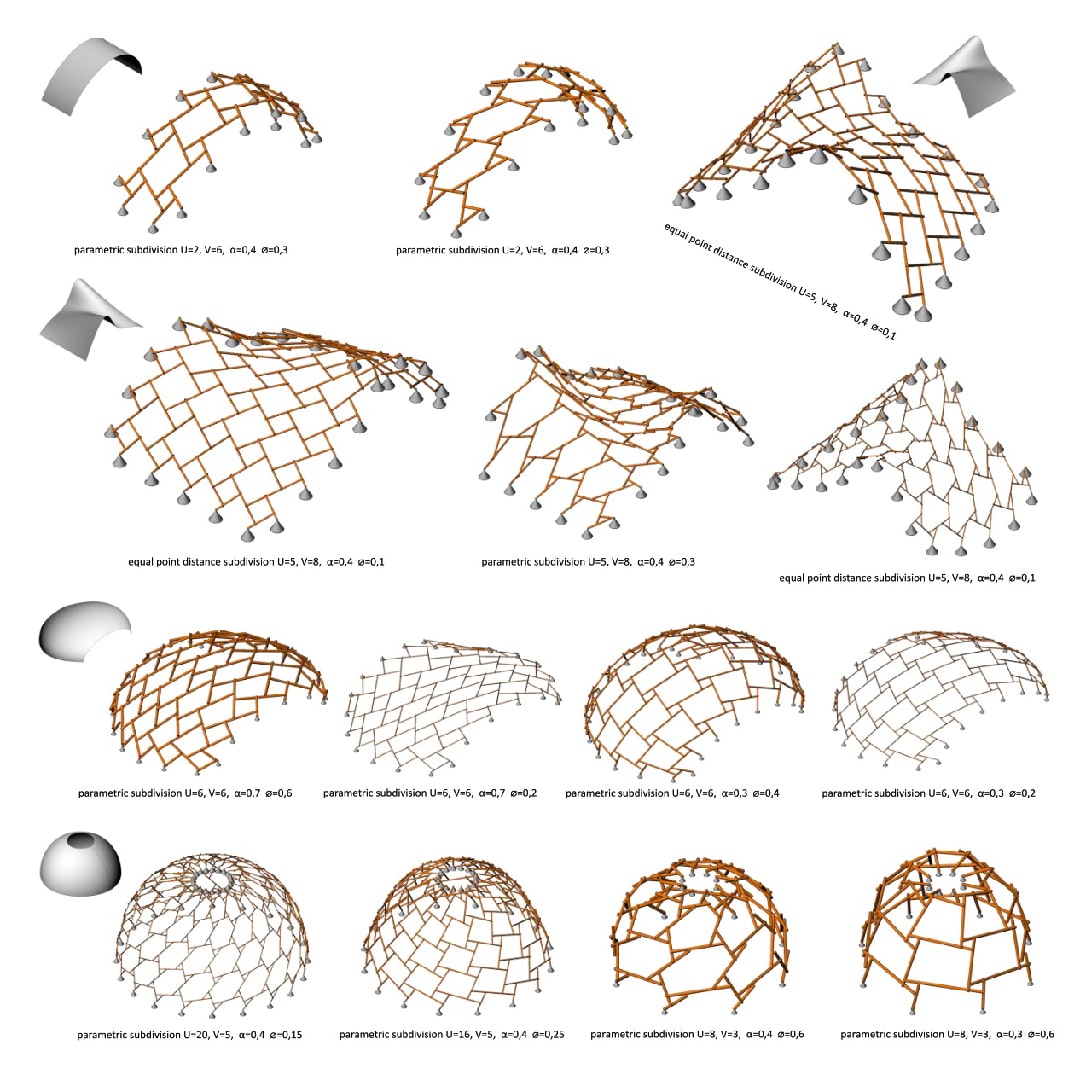
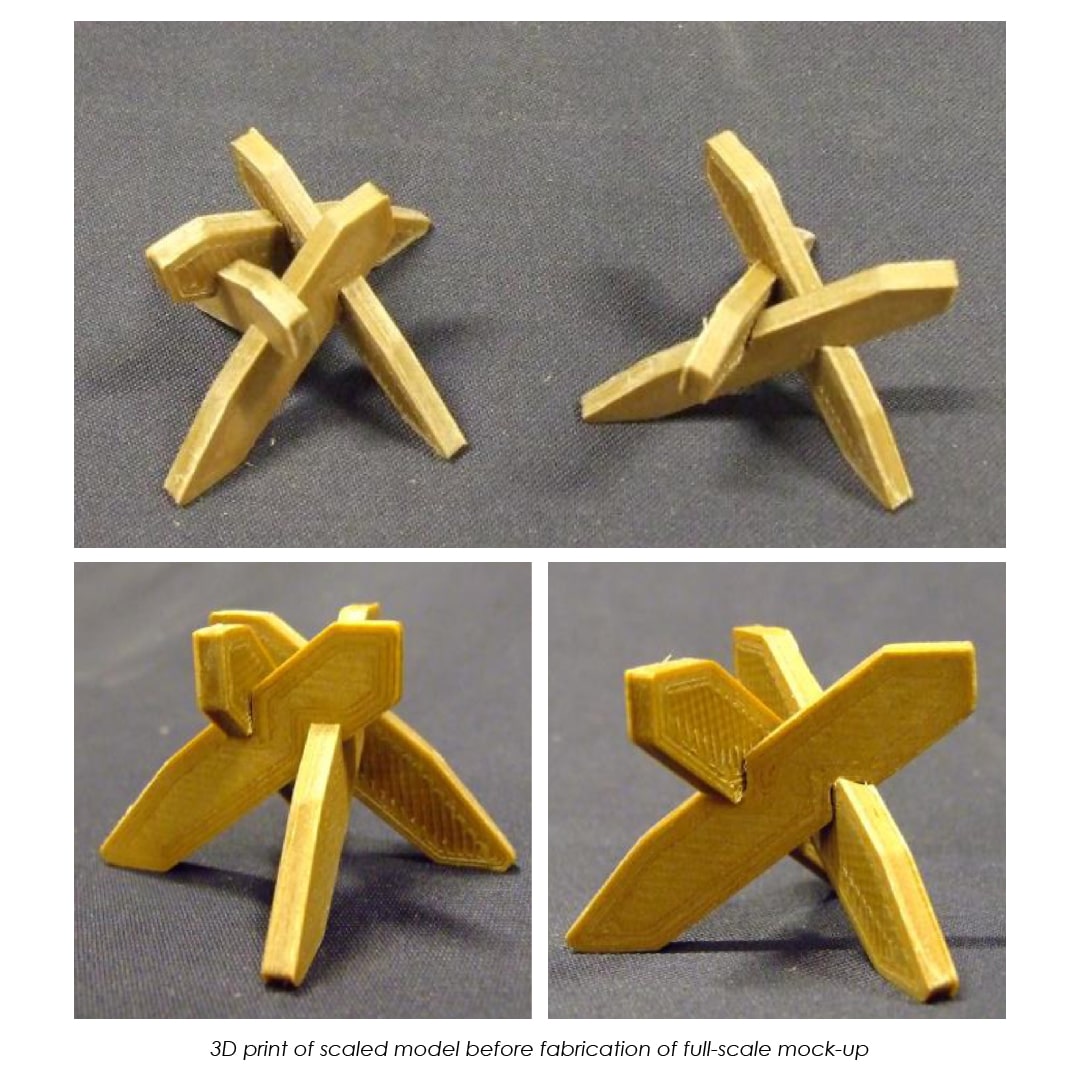
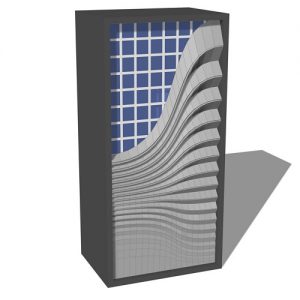
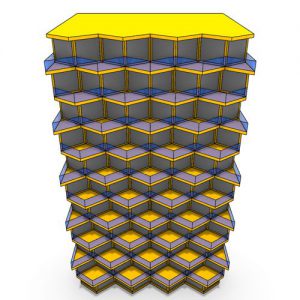
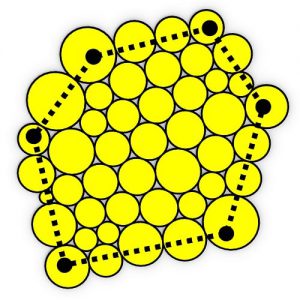
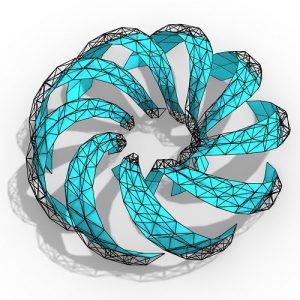
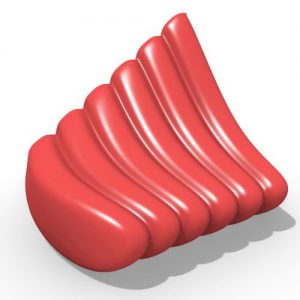
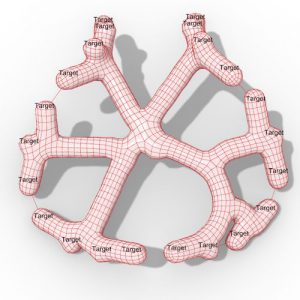
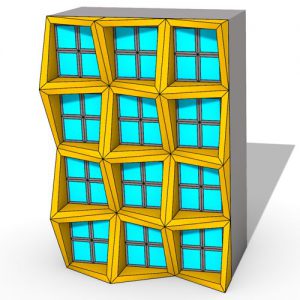
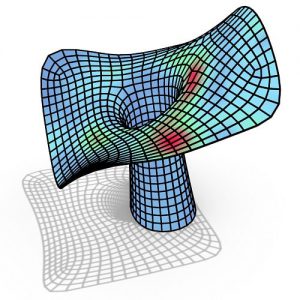
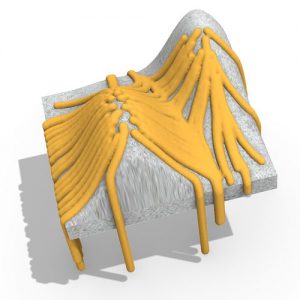
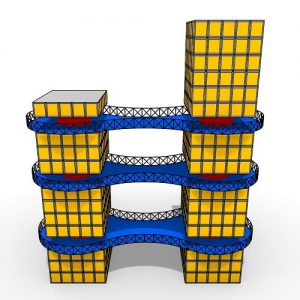
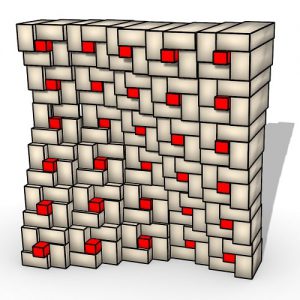
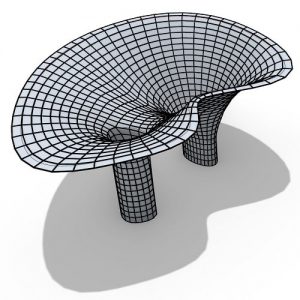
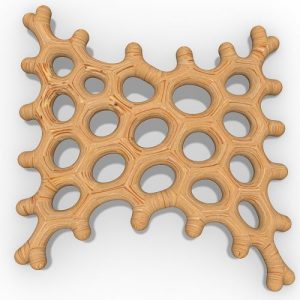
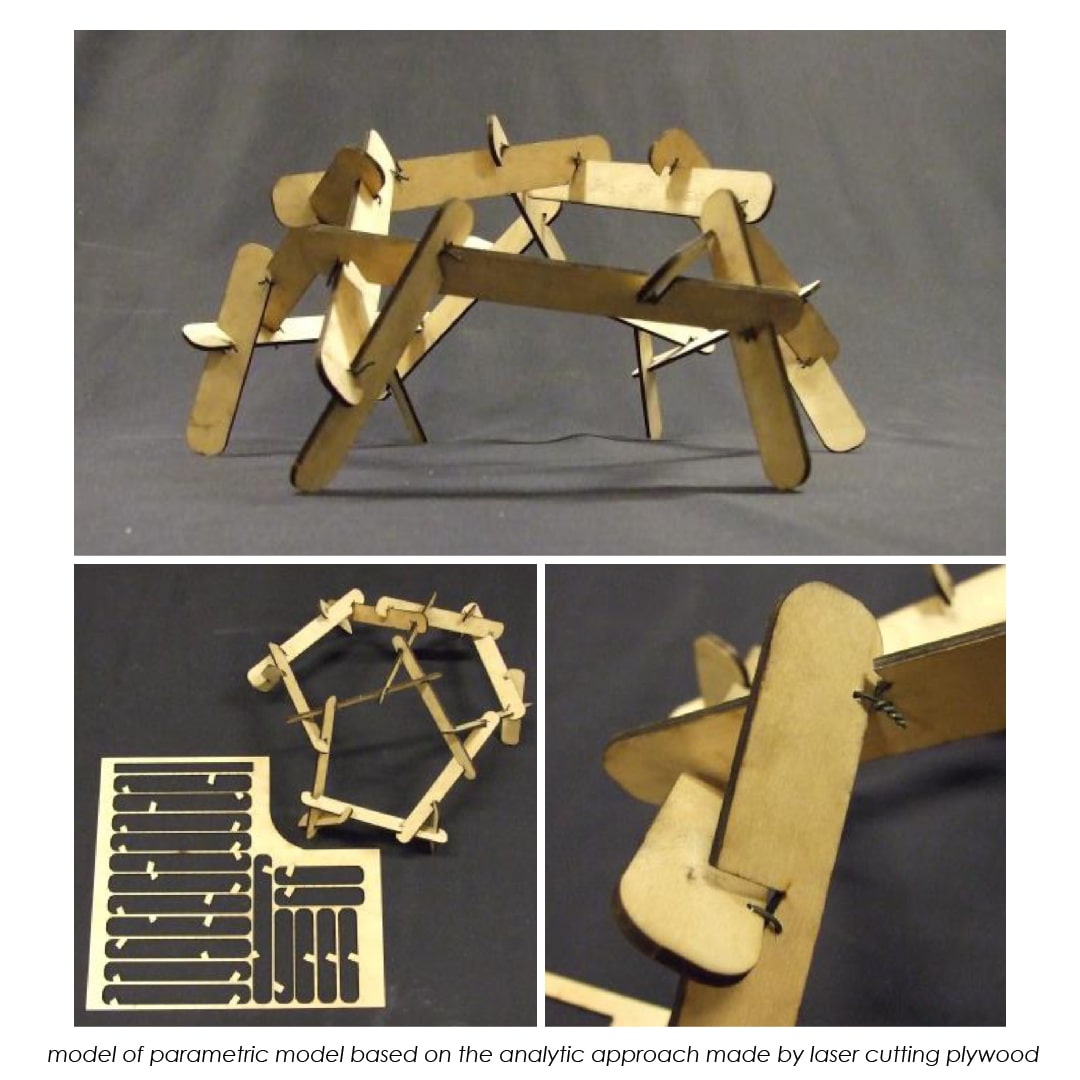 An experimental validation of the design to production process is made by means of a full-scale model, built in cooperation with the timber industry. Three resulting RF designs made with the RFD are displayed above.
An experimental validation of the design to production process is made by means of a full-scale model, built in cooperation with the timber industry. Three resulting RF designs made with the RFD are displayed above.
 The choose for timber in RFs has economic and implementation arguments for the building industry: short lengths, inferior scrap wood, slender and buckling sensitive sheet materials, recycled wood, locally grown wood species, can all be used in RF structures and are often less sought after. It shows that the RF principle lends itself for using residual flows from industrial timber production.
The choose for timber in RFs has economic and implementation arguments for the building industry: short lengths, inferior scrap wood, slender and buckling sensitive sheet materials, recycled wood, locally grown wood species, can all be used in RF structures and are often less sought after. It shows that the RF principle lends itself for using residual flows from industrial timber production.
 From designing RFs to the choice of the main material, this introduction discusses the literature study topics. Moreover, it results in the aim of this graduation project which is to develop a computational RF structural design tool using an optimal jointing system and a sustainable timber-based material.
From designing RFs to the choice of the main material, this introduction discusses the literature study topics. Moreover, it results in the aim of this graduation project which is to develop a computational RF structural design tool using an optimal jointing system and a sustainable timber-based material.
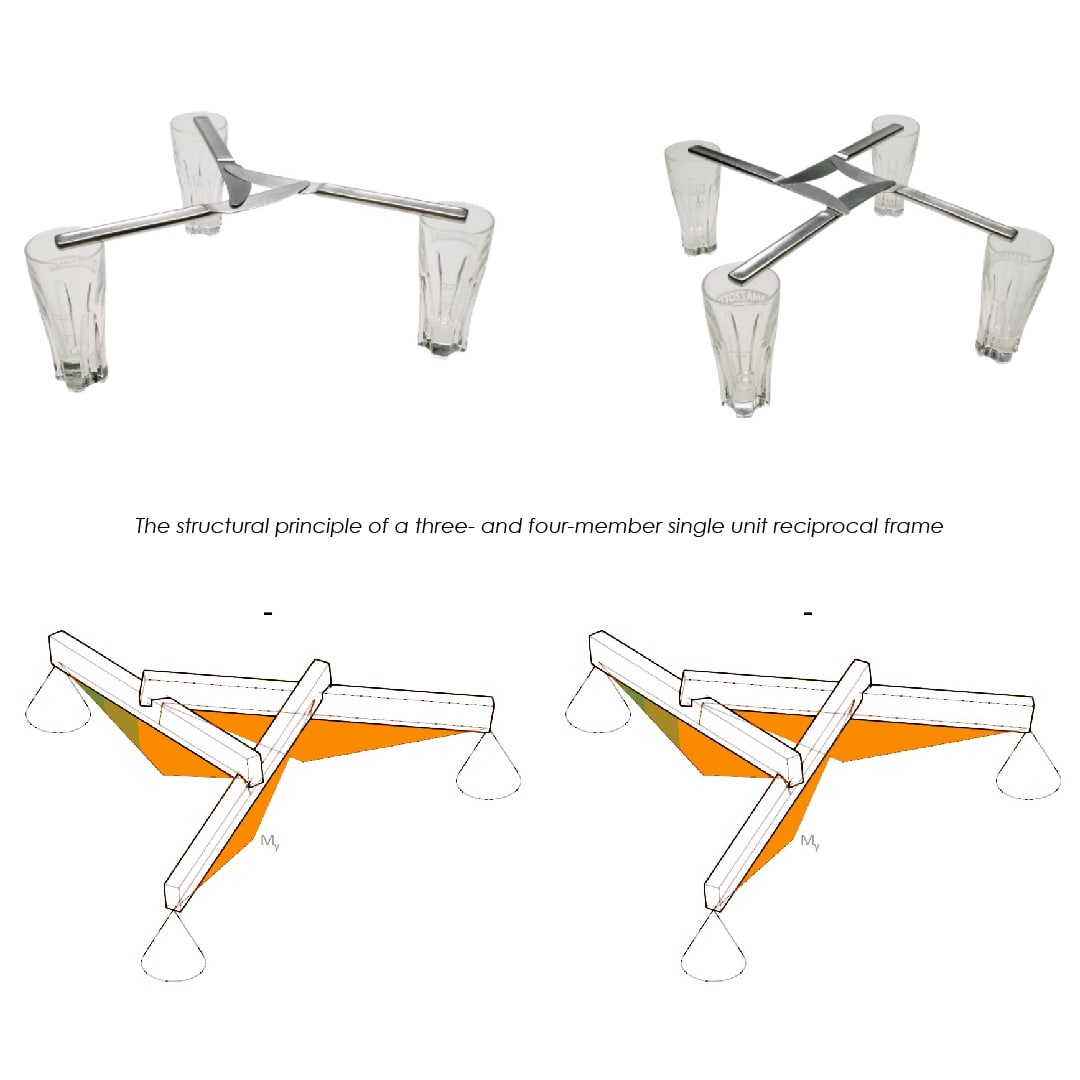 This could lead to the creation of a sustainable timber RF structure. The following study provides the theoretical knowledge to achieve this aim.
This could lead to the creation of a sustainable timber RF structure. The following study provides the theoretical knowledge to achieve this aim.










Comments
ESaliklis
Can we see the GH script?
rezae
Hi, You can use Ngon plugin
AhHussein
link not working!
parametric
The link has been updated…thanks for reporting