Topology Optimization
An Architectural Implementation
of Topology Optimization Guided Discrete Structures
with Customized Geometric Constraints
Soo Jung Woo
A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo
in fulfillment of the thesis requirements for the degree of
Master of Architecture

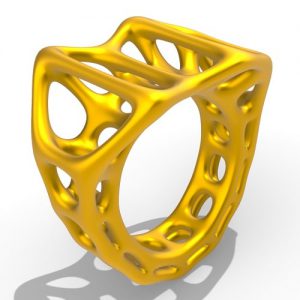
This thesis by Soo Jung Woo explores the use of Topology Optimization (abbreviated to TO) in architectural design by implementing a Bidirectional Evolutionary Structural Optimization(abbreviated to BESO) type TO script as a guide to create a composition of discrete members with complex geometries.

TO is an efficient tool for generating an optimal spatial arrangement of structural members along a load path. In the field of computational design, TO has been employed for form-generation of a range of assembled structures that employ discrete units, as well as continuum structures that employ unified and continuous materials.
The most advanced current architectural implementations for continuum structures appear in the design of connections, and for discrete structures within space truss designs. Yet, the use of TO in atypical discrete frame structures with complex geometries remain relatively undeveloped in contemporary practice.

This thesis contributes a case study where TO is implemented at two key scales: at the component level, geometrically constrained discrete components are assembled using TO, at the macro level, these components are arranged over a TO-designed body. A review of literature from computational design and structural engineering fields, discussing current TO implementations, as well as presenting case studies, is included.

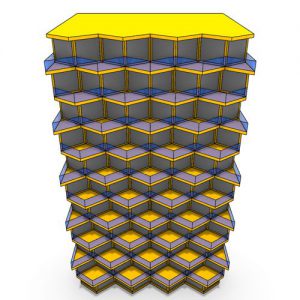
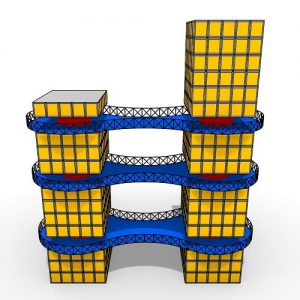
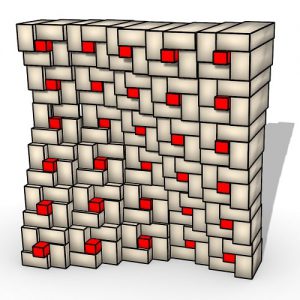
The demonstration within the thesis presents a contemporary architectural design process by using existing Karamba BESO code components within a Grasshopper parametric script. Fine-grained components employed within the facade system are combined using TO to produce a cellular lattice architectonic assembly that refers to traditional Korean ornamental pattern found near the site. This demonstration is evaluated structurally and aesthetically.
Analyses of comparative structural models with varying configurations are used to demonstrate
the structural efficiency of the proposed design. For the aesthetic evaluation, a series of drawings are included to demonstrate what type of spatial qualities the customized lattice structure would look like. The goal of this thesis is to demonstrate architectural and structural qualities resulting from a hybrid exercise where a TO process is applied to geometrically constrained discrete structures.
The approach in this thesis provides compromises where structural efficiency and aesthetics are both reasonably achieved, and may lead to novel designs. Future work could be to create a new TO algorithm that can automate this process for increased structural efficiency.










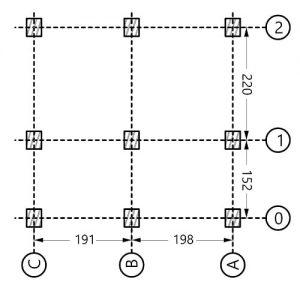

Comments