String Art Generator
String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can
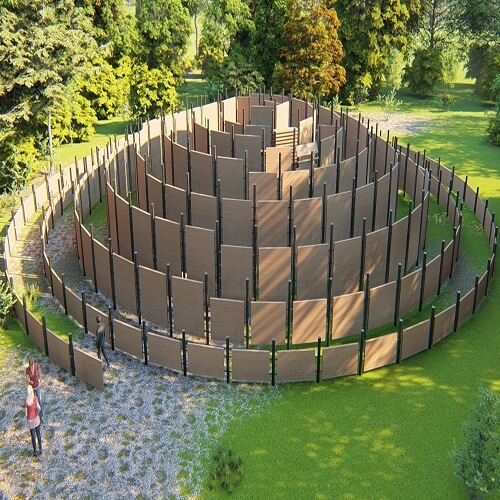

Cognizant Architecture is a term used to define sentient and smart structures broadly. In this paper by Sobia Ilyas, Xinyue Wang, Wenting Li, Zhuoqun Zhang, Tsung-Hsien Wang and Chengzhi Peng, an `Interactionist’ model of cognizant architecture is proposed as a method of investigating the development process by inverting the conventional concept of maze design.
 The proposed `Cognizant Maze’ aims to achieve user-architecture micro-interactions through delighting the users, presenting a physical activity equally attractive to kids and adults alike, and activating mind-enticing visual effects. Like many previous innovations, nature is what inspires us in the maze-making process.
The proposed `Cognizant Maze’ aims to achieve user-architecture micro-interactions through delighting the users, presenting a physical activity equally attractive to kids and adults alike, and activating mind-enticing visual effects. Like many previous innovations, nature is what inspires us in the maze-making process.
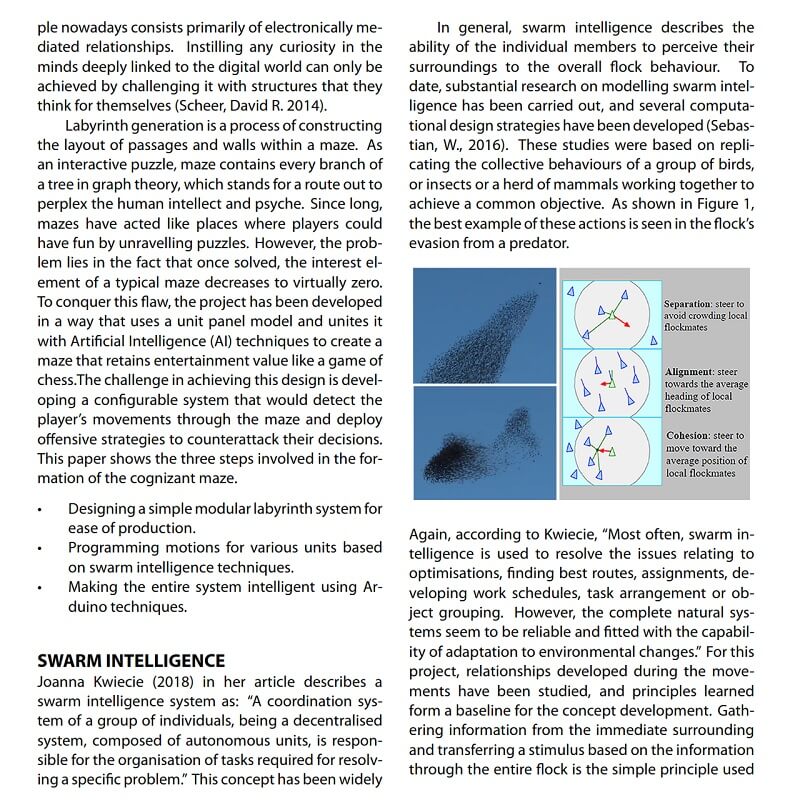
 In modelling the cognizant maze, authors develop the concept and workflow of prototyping a form of swarm intelligence. Authors are particularly interested in exploring how simulated behaviours of swarm intelligence can be manifested in a maze environment for micro-interactions to take place.
In modelling the cognizant maze, authors develop the concept and workflow of prototyping a form of swarm intelligence. Authors are particularly interested in exploring how simulated behaviours of swarm intelligence can be manifested in a maze environment for micro-interactions to take place.
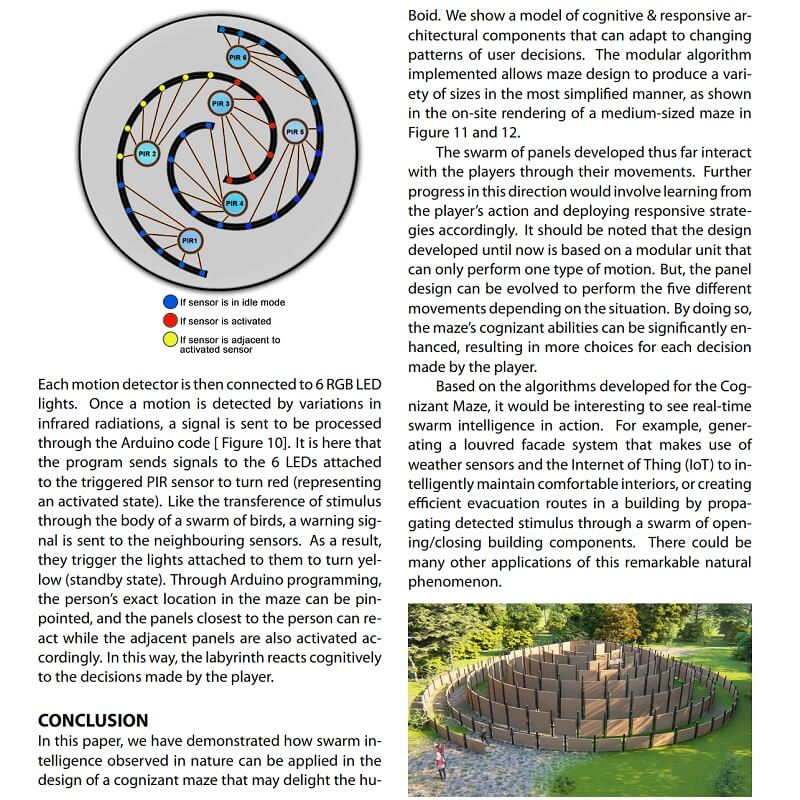
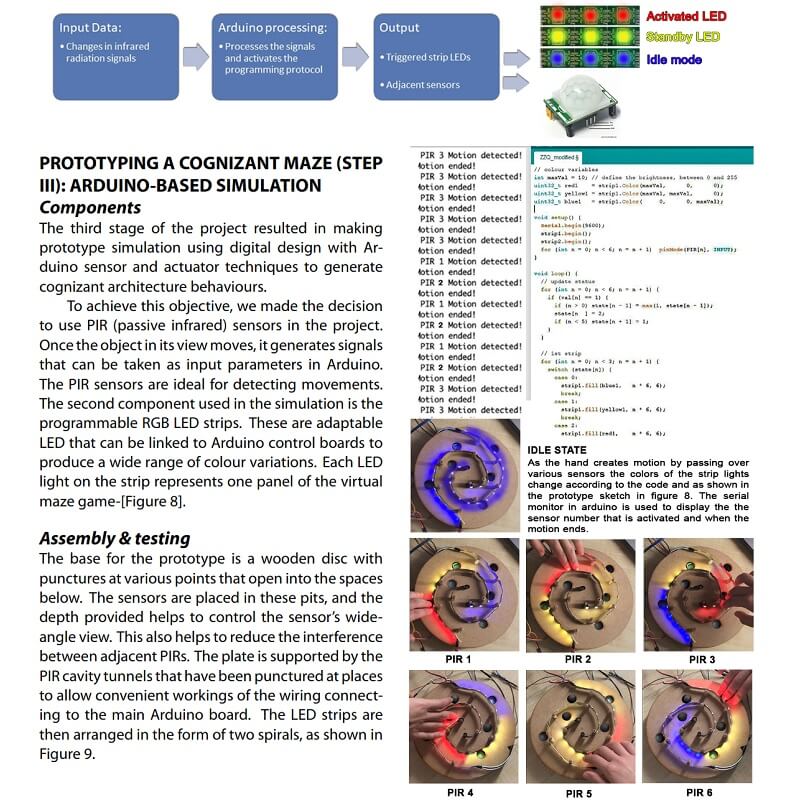 Combining parametric modelling and Arduino-based physical computing, this interactive prototyping shows how the maze and its users can `think, act and play’ with each other, hence achieving an interactionist model of cognizant architecture. Authors reflect that the lessons learned from the Cognizant Maze experiment may lead to further development of cognizant architecture as a propagation of swarm intelligence through multi-layered micro-interactions.
Combining parametric modelling and Arduino-based physical computing, this interactive prototyping shows how the maze and its users can `think, act and play’ with each other, hence achieving an interactionist model of cognizant architecture. Authors reflect that the lessons learned from the Cognizant Maze experiment may lead to further development of cognizant architecture as a propagation of swarm intelligence through multi-layered micro-interactions.

String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can

This paper by Alessandro Liuti, Sofia Colabella, and Alberto Pugnale, presents the construction of Airshell, a small timber gridshell prototype erected by employing a pneumatic formwork.

In this paper by Gregory Charles Quinn, Chris J K Williams, and Christoph Gengnagel, a detailed comparison is carried out between established as well as novel erection methods for strained grid shells by means of FE simulations and a 3D-scanned scaled physical model in order to evaluate key performance criteria such as bending stresses during erection and the distance between shell nodes and their spatial target geometry.

In this paper by Frederic Tayeb, Olivier Baverel, Jean-François Caron, Lionel du Peloux, ductility aspects of a light-weight composite gridshell are developed.
Parametric Ideas for Architects @2025
This tutorial or example file is exclusive to Paracourse Members.
Paracourse is an extensive library of video tutorials and example files, designed to guide you through your parametric design journey. With over 1,500 open example files & 600 Video Tutorials, you can freely edit and adapt them for your projects—no credit required.

Learn parametric design from scratch with over 100 hours of step-by-step tutorials, covering beginner to intermediate levels. Master components and their use in the design process.

Explore our open-to-edit .gh files to see how each subject is designed parametrically using Grasshopper3D. Freely adapt them for your projects—no credit required.

Delve into complete algorithms with our advanced tutorials. Learn the logic behind each step, understand how the parts work together, and see how to apply them effectively in your designs.
Grasshopper empowers architects and designers to create sophisticated, customizable designs with ease.
Architects, industrial designers, artists, and anyone passionate about parametric design will find value in this course.
With diverse tutorials and open example files, you’ll have everything you need to tackle any design challenge.
Mastering Grasshopper with Paracourse can significantly enhance your career prospects.