String Art Generator
String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can
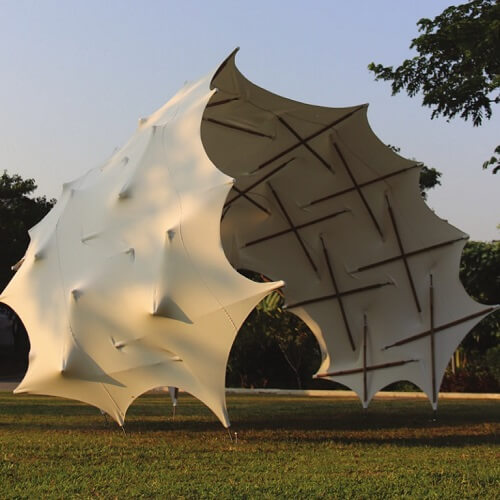


Structural membranes exhibit advantages over slab and frame structures, accommodating large deformations while still elegantly combining spatial enclosure with material efficiency. One of the most promising types of membrane structures are membrane tensegrity structures, which are composed of discontinuous struts embedded in a tensile membrane. To date, membrane tensegrity structures are limited to completely closed formations or require extensive tethering, hindering their applicability for diverse architectural contexts.
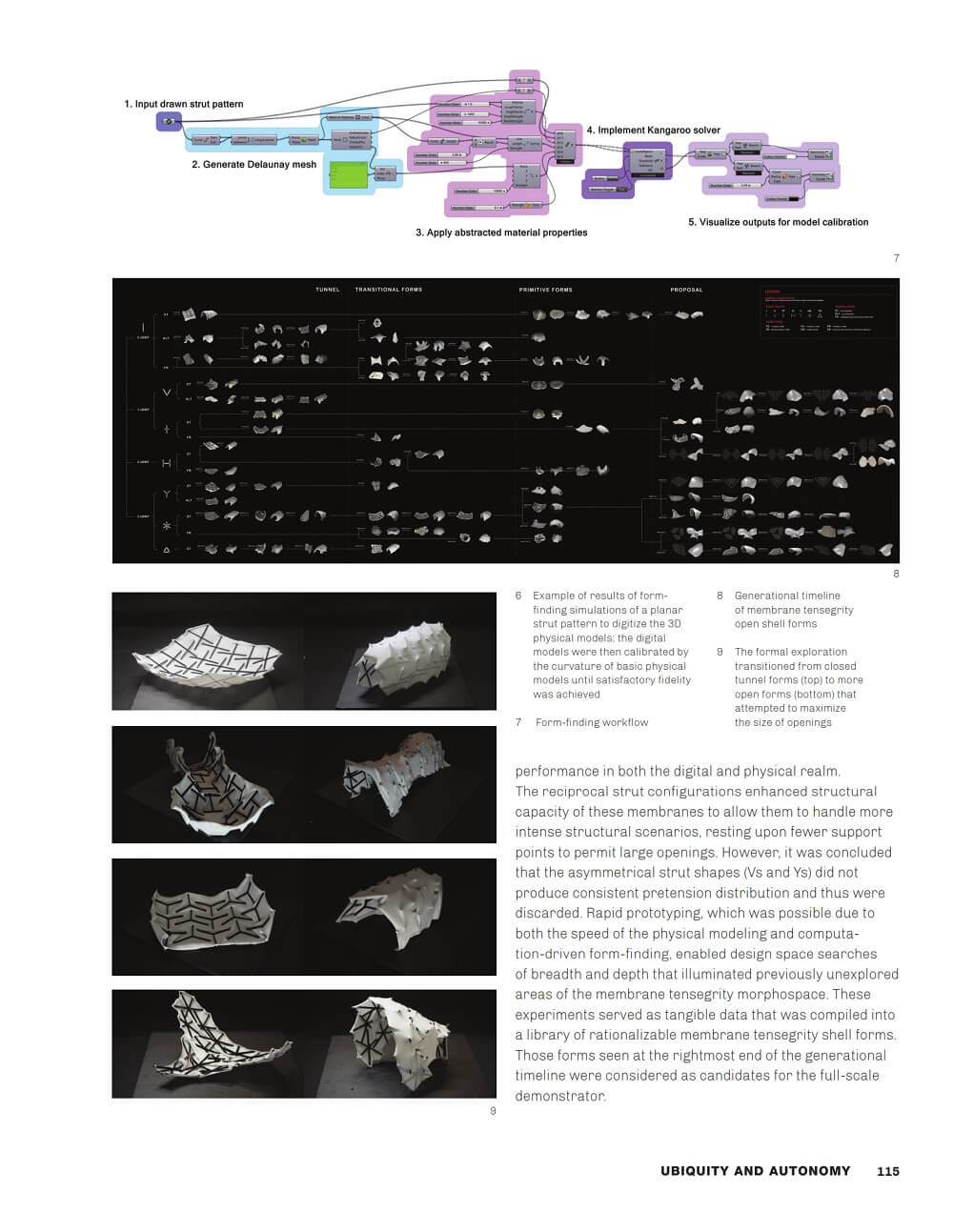
In this article by Kenneth Tracy, So Jing Wen, Sachin Sean Gupta, Abhipsa Pal, Loo Yi Ning Stella, Thomas Wortmann and Robert Bamford; a design framework is presented for creating self-supporting membrane tensegrity shell structures with spatial openings, enabled by novel reciprocally tessellated strut configurations. Through a combination of heuristic physical prototyping and digital formfinding tools, a library of membrane tensegrity forms has been developed that serves as tangible data for an expanded morphospace.
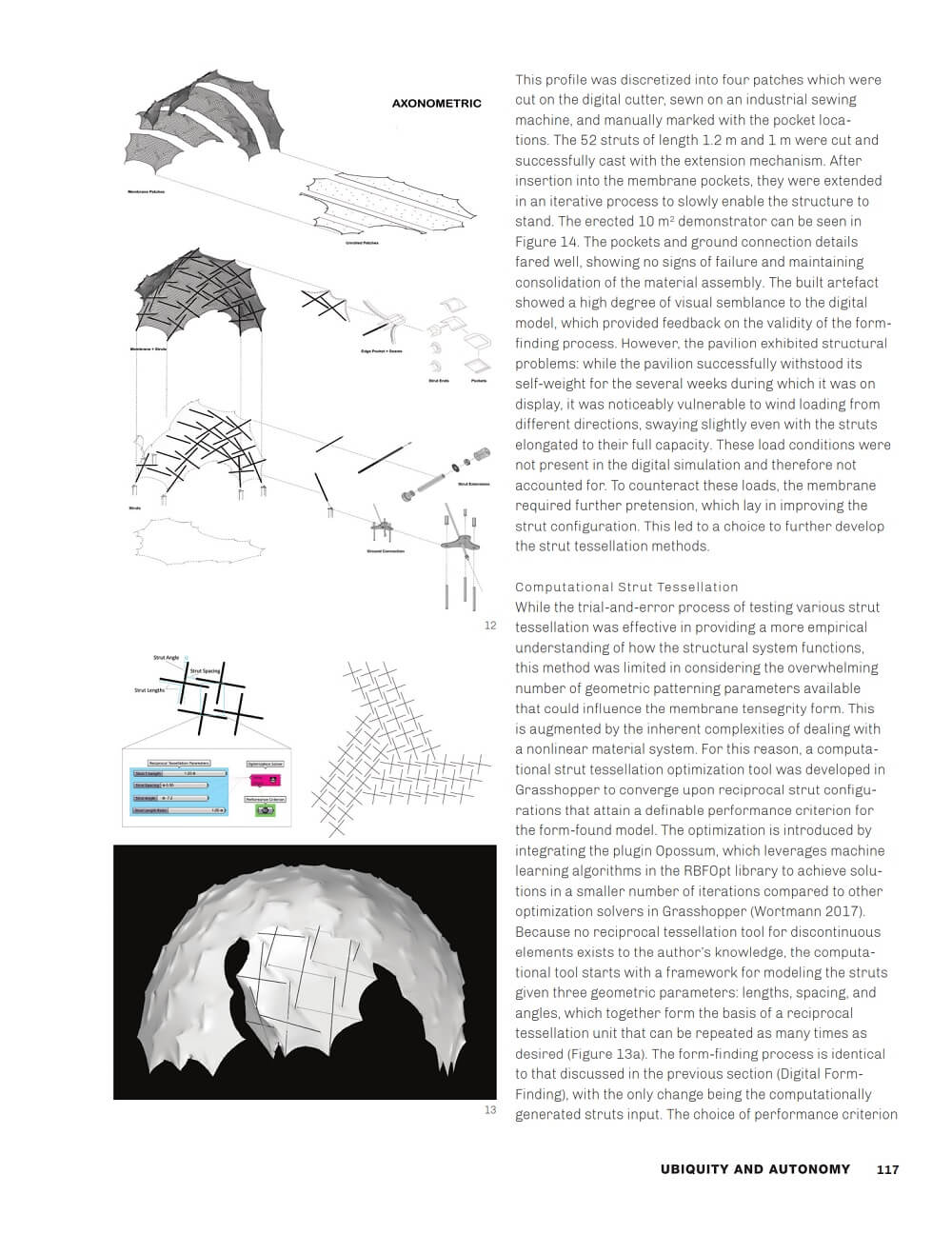
To test the effectiveness of the established methods, a 10 m2 membrane tensegrity shell pavilion was built as a first large-scale demonstrator. Feedback from this demonstrator led to the development of computational strut tessellation tools that enable the search for informed, performance-driven design space.


String Art Generator by Yiran is a grasshopper plugin which generates a string art sequence based on an input image. You can

This paper by Alessandro Liuti, Sofia Colabella, and Alberto Pugnale, presents the construction of Airshell, a small timber gridshell prototype erected by employing a pneumatic formwork.

In this paper by Gregory Charles Quinn, Chris J K Williams, and Christoph Gengnagel, a detailed comparison is carried out between established as well as novel erection methods for strained grid shells by means of FE simulations and a 3D-scanned scaled physical model in order to evaluate key performance criteria such as bending stresses during erection and the distance between shell nodes and their spatial target geometry.

In this paper by Frederic Tayeb, Olivier Baverel, Jean-François Caron, Lionel du Peloux, ductility aspects of a light-weight composite gridshell are developed.
Parametric Ideas for Architects @2025