Adaptive Kinetic Patterns
Design strategy for adaptive kinetic patterns: creating agenerative design for dynamic solar shading systems
By: Jamil Majed Jamil Alkhayyat
September 2013
 This dissertation discusses the role of designing adaptive kinetic patterns in architecture, architectural surfaces have been covered by patterns long time ago, and the problem is how kinetic adaptive patterns will be designed for improving the sustainability of buildings by providing a proper daylighting, there is no clear strategy for designing these kinetic patterns as it is still new to the field of architecture.
This dissertation discusses the role of designing adaptive kinetic patterns in architecture, architectural surfaces have been covered by patterns long time ago, and the problem is how kinetic adaptive patterns will be designed for improving the sustainability of buildings by providing a proper daylighting, there is no clear strategy for designing these kinetic patterns as it is still new to the field of architecture.
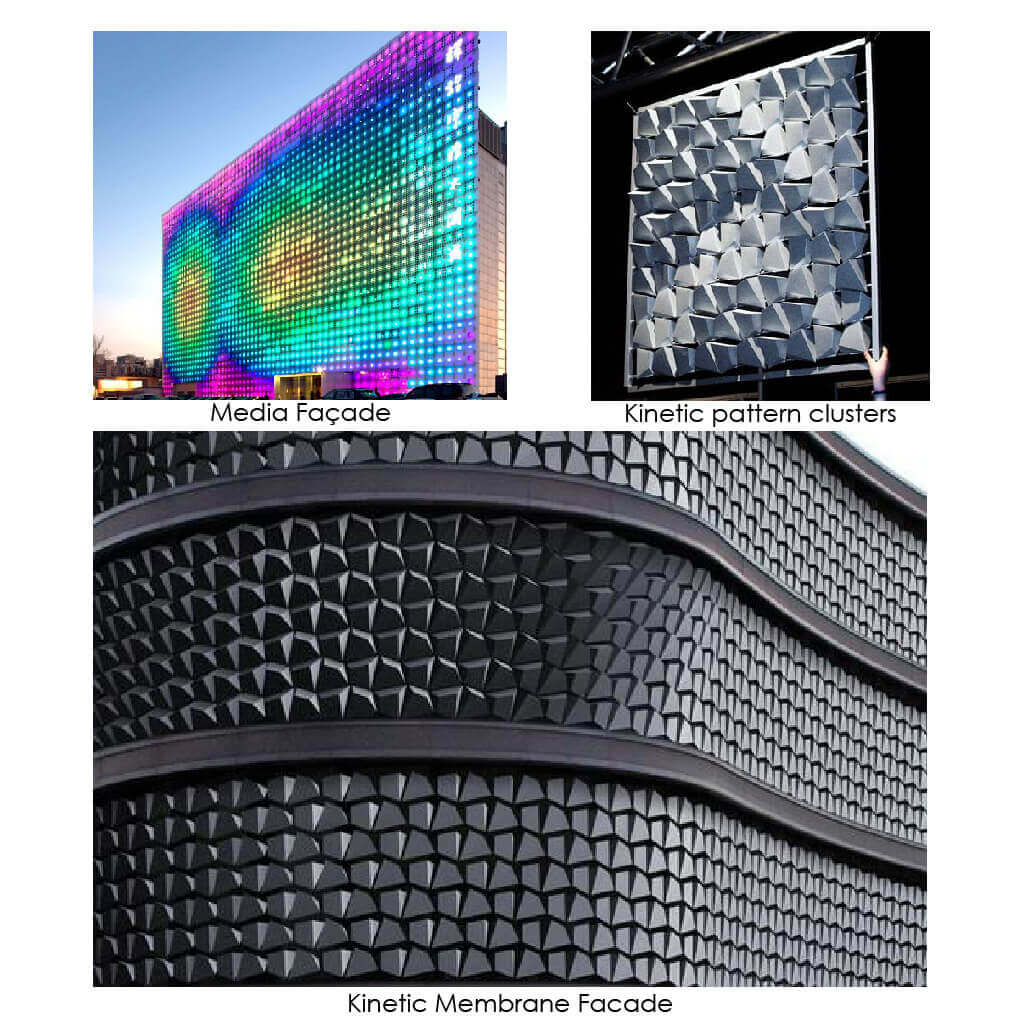 Creating design strategy will be done by analysing theories for designing this kind of patterns, extracting outcomes and design strategies from case studies, reinforcing the creation of the design strategy by design implementation.
Creating design strategy will be done by analysing theories for designing this kind of patterns, extracting outcomes and design strategies from case studies, reinforcing the creation of the design strategy by design implementation.
*Pix
This research results indicated that the process of designing adaptive kinetic patterns has five phases: Design generation, Technology, Rationalization, Mechanism, and Materialization. Starting by design approach and specifications of the formal aspects of the designer, and how the designed pattern has been represented for following stages.
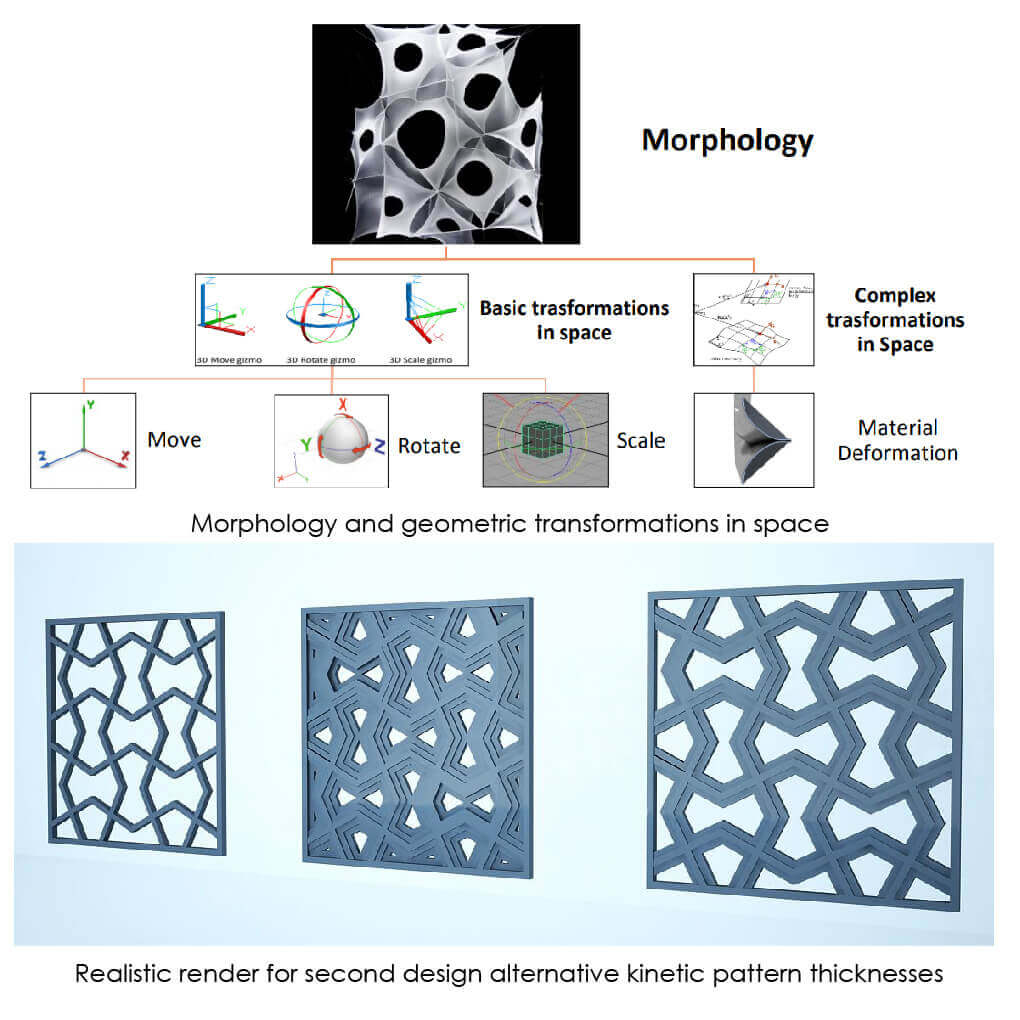 Transforming the free-form and conceptual sketches into rational adaptive kinetic pattern joined with a supporting structure. Then selection of the technical machines aspects, processes, tools, systems and strategies. And finally taking decisions regarding the formal and interactive attributes of the structural system, the elements, and selecting materials.
Transforming the free-form and conceptual sketches into rational adaptive kinetic pattern joined with a supporting structure. Then selection of the technical machines aspects, processes, tools, systems and strategies. And finally taking decisions regarding the formal and interactive attributes of the structural system, the elements, and selecting materials.
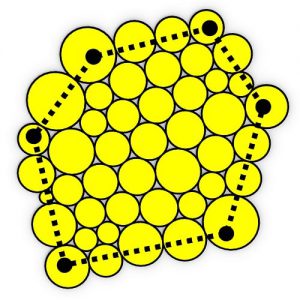
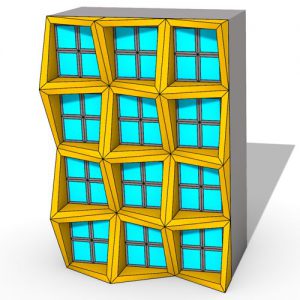
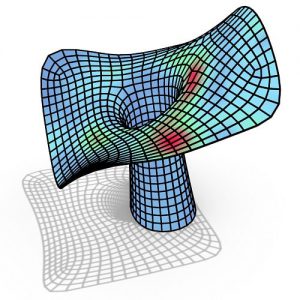
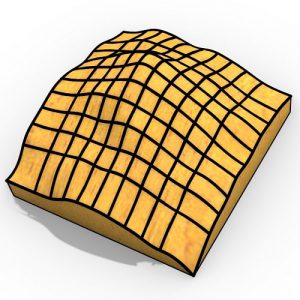
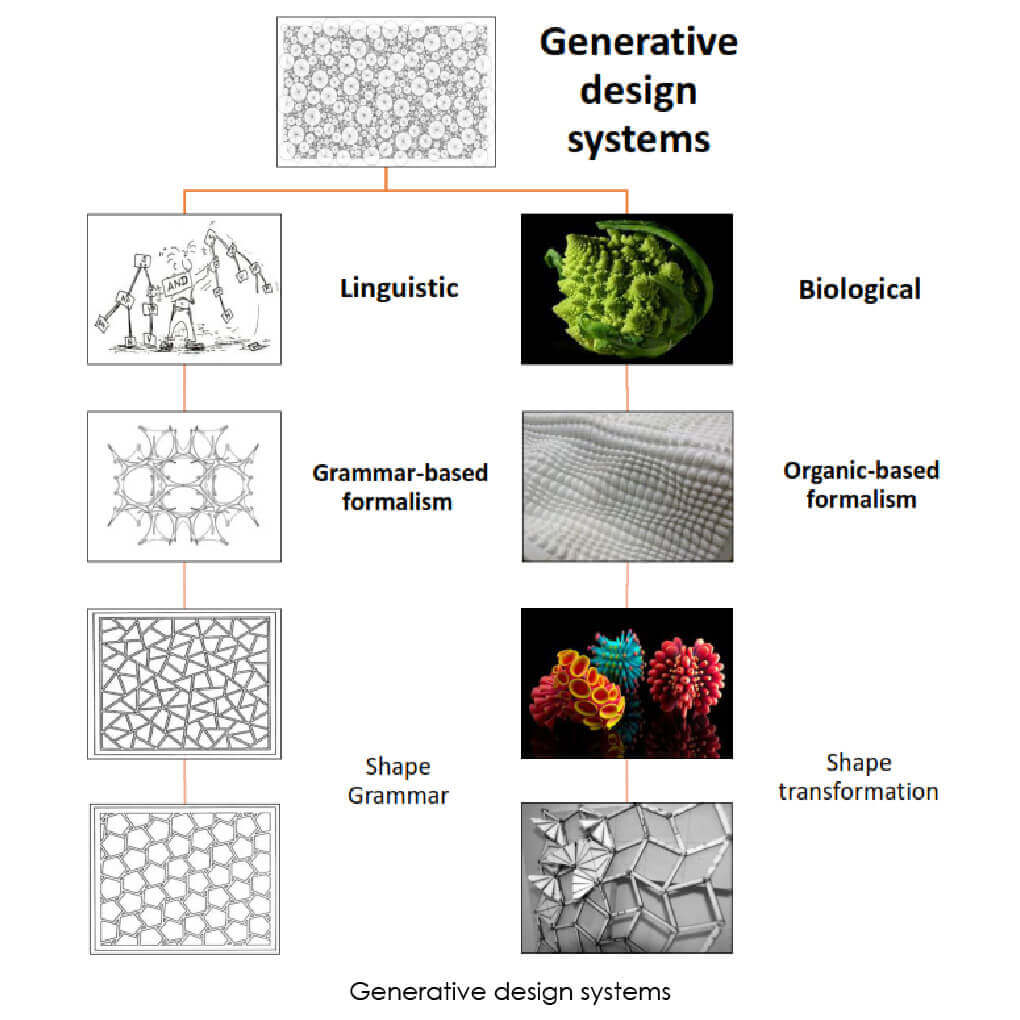 All of the fundamental various kinds of patterns which could be shaped by identical tiles were found in the thirteenth century at Alhambra Palace in Granada, Andalusia, Spain, the mathematical categorizing has been actually done in the twentieth century. Present-day architecture produces a fabulous variation of new designs and three-dimensional patterns, however, architects probably will not always obtain the suitable tools at their disposal to recognize this kind of structures, this is a difficult and fascinating activity for mathematicians to fill the disparity between design and construction and innovate brand-new fabrication aware design tools for architectural software. Patterns are a tremendous field, even in architecture they are presented in many different software programs.
All of the fundamental various kinds of patterns which could be shaped by identical tiles were found in the thirteenth century at Alhambra Palace in Granada, Andalusia, Spain, the mathematical categorizing has been actually done in the twentieth century. Present-day architecture produces a fabulous variation of new designs and three-dimensional patterns, however, architects probably will not always obtain the suitable tools at their disposal to recognize this kind of structures, this is a difficult and fascinating activity for mathematicians to fill the disparity between design and construction and innovate brand-new fabrication aware design tools for architectural software. Patterns are a tremendous field, even in architecture they are presented in many different software programs.
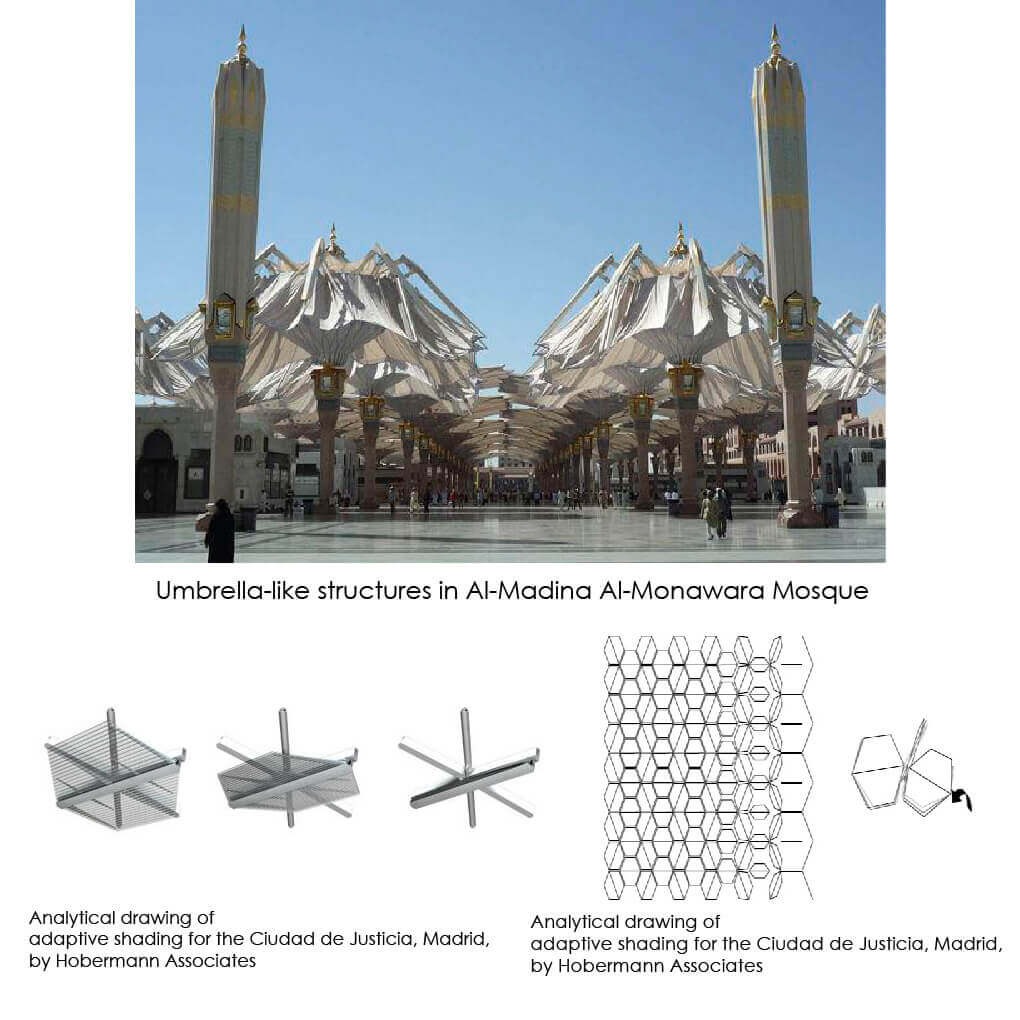
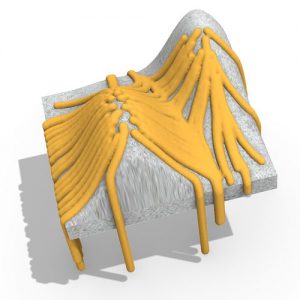
Within present-day architecture there is a rising concern in kinetics. As verified by smart facades, the potentials are for a responsive skin that adapts to varying environment situations and user residence.
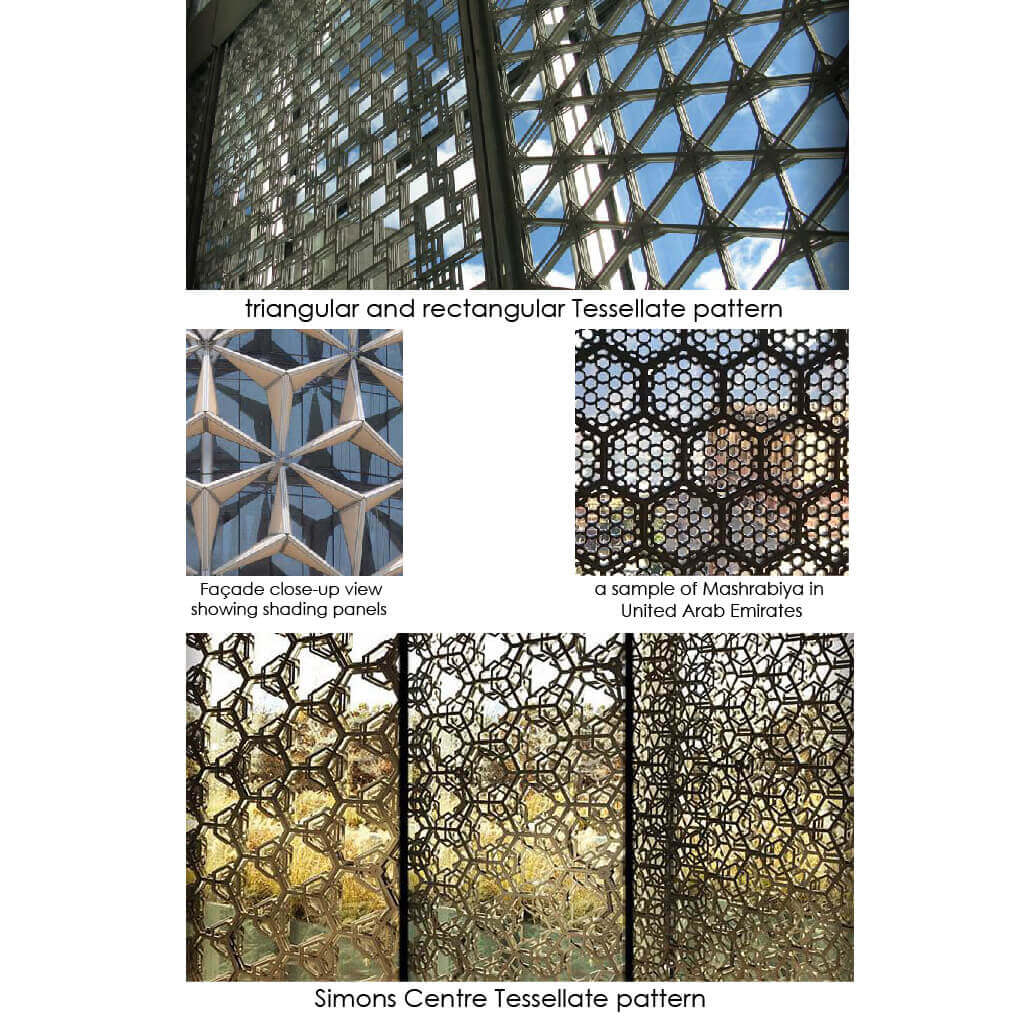 The world of Patterns is one of the latest and fastest growing fields in architecture nowadays; many designers are creating a combination between patterns with software, sensors, and robotics, whether their focus are visual appearance or sustainability terms. Therefore, the justification for adaptive kinetic patterns is founded in the following reasons: economy of means, responsive towards the natural environment, and the satisfaction of human needs and desires. Developing daylighting usage decreases the requirement for artificial lighting and cooling, and has the ability for reducing energy costs by thirty to seventy percent. It also grants buildings more gorgeous, and increases occupants’ healthiness and productivity.
The world of Patterns is one of the latest and fastest growing fields in architecture nowadays; many designers are creating a combination between patterns with software, sensors, and robotics, whether their focus are visual appearance or sustainability terms. Therefore, the justification for adaptive kinetic patterns is founded in the following reasons: economy of means, responsive towards the natural environment, and the satisfaction of human needs and desires. Developing daylighting usage decreases the requirement for artificial lighting and cooling, and has the ability for reducing energy costs by thirty to seventy percent. It also grants buildings more gorgeous, and increases occupants’ healthiness and productivity.
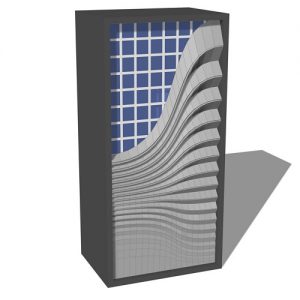
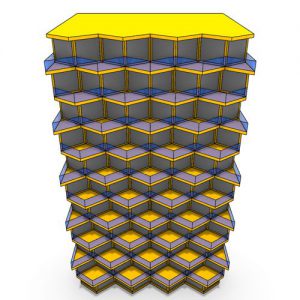
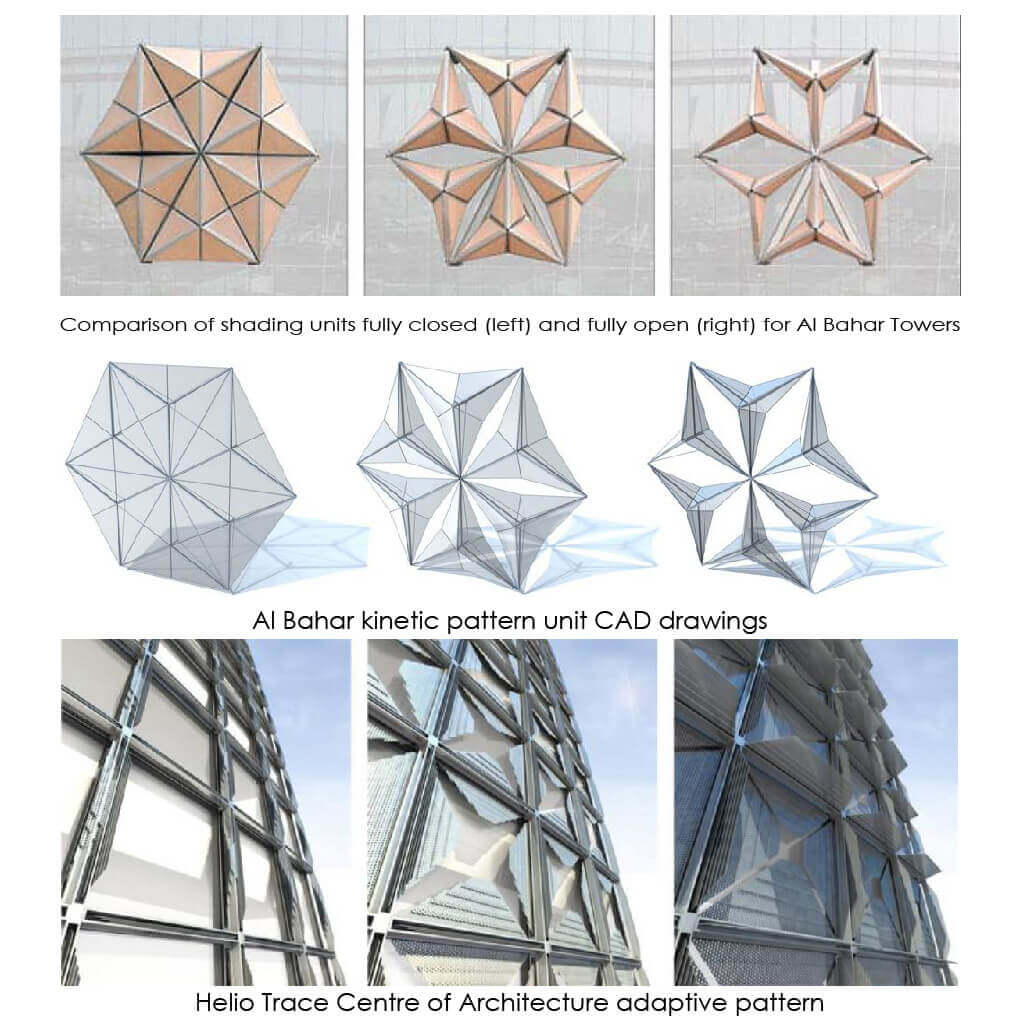 Adaptive kinetic patterns design is still new in architecture and three-dimensional modelling field, an appropriate strategy for design these pattern is needed, in order to help designers improving their design skills and learn about this new field. Kinetic structures needed to be modelled by a parametric generative modelling software, because they do not have a single form, but a continuous revolving shapes.
Adaptive kinetic patterns design is still new in architecture and three-dimensional modelling field, an appropriate strategy for design these pattern is needed, in order to help designers improving their design skills and learn about this new field. Kinetic structures needed to be modelled by a parametric generative modelling software, because they do not have a single form, but a continuous revolving shapes.
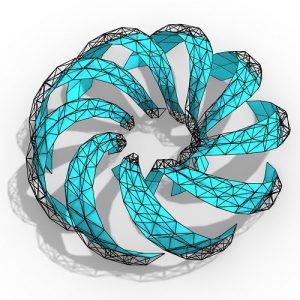
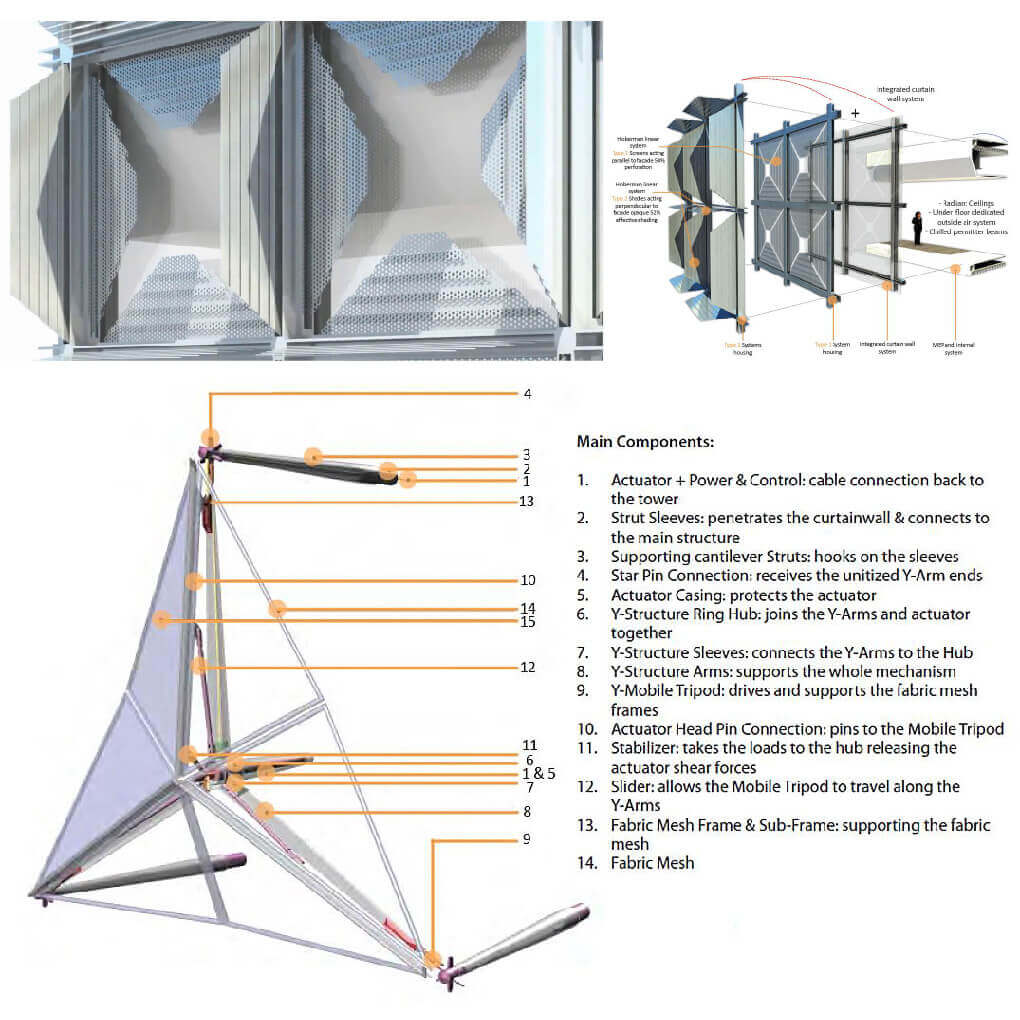 Designing through parametric generative tool is one of the main steps that should be considered when proposing and designing a kinetic element. The Potential of designing kinetic building elements using a parametric generative design tool is not explored in detail so far, and it is needed; in order to have a creative efficient adaptive design.
Designing through parametric generative tool is one of the main steps that should be considered when proposing and designing a kinetic element. The Potential of designing kinetic building elements using a parametric generative design tool is not explored in detail so far, and it is needed; in order to have a creative efficient adaptive design.
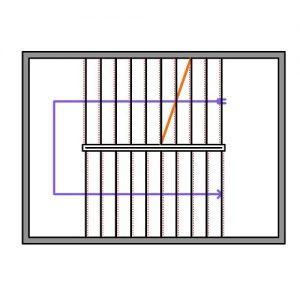
 For technology aspect, every design has its own design kinetic features, it depends on design needs. All the designs have sun tracking sensors or a time schedule for sun path, it is an essential aspect for designing kinetic adaptive patterns.
For technology aspect, every design has its own design kinetic features, it depends on design needs. All the designs have sun tracking sensors or a time schedule for sun path, it is an essential aspect for designing kinetic adaptive patterns.











Comments