Thermal Biomimetic
Enhancing Thermal performance Of Building Envelope using Biomimetic optimization algorithms
By: Wael Salah Mansour Abdelrahman
2021
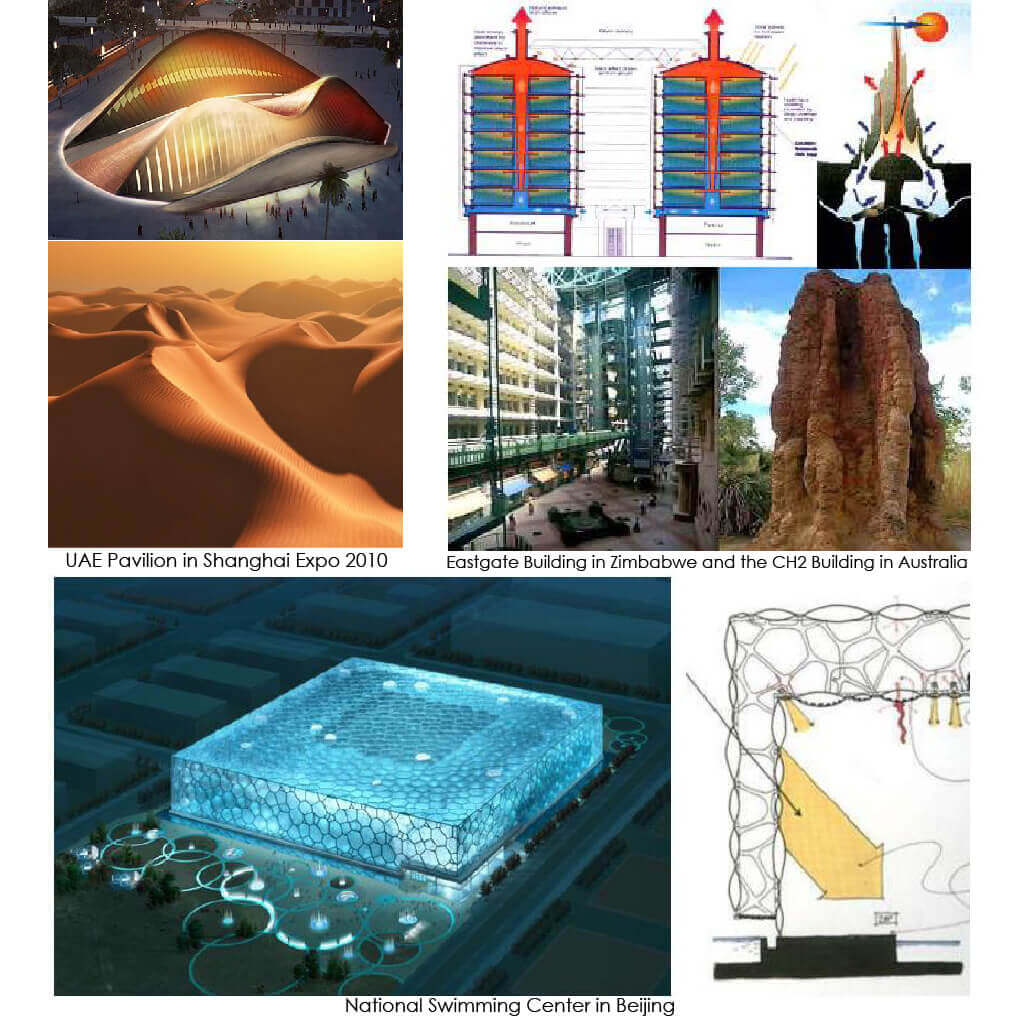 Building envelope is the first defense line of the indoor environment in the inevitable confrontation with the outdoor environment. The main factors used for the definition of Building envelope are its function, characteristics, and impacts on whole buildings. The primary and main functions of the building envelope are to provide security and shelter. Building envelope helps in achieving comfort in built environment spaces such as daylight, thermal, acoustic, solar, indoor air quality, fire resistance, and moisture control. Building envelope is considered an essential pillar for achieving thermal comfort for the quality of the indoor environment of buildings. Building envelope contributes to providing a built environment with aesthetic quality as well.
Building envelope is the first defense line of the indoor environment in the inevitable confrontation with the outdoor environment. The main factors used for the definition of Building envelope are its function, characteristics, and impacts on whole buildings. The primary and main functions of the building envelope are to provide security and shelter. Building envelope helps in achieving comfort in built environment spaces such as daylight, thermal, acoustic, solar, indoor air quality, fire resistance, and moisture control. Building envelope is considered an essential pillar for achieving thermal comfort for the quality of the indoor environment of buildings. Building envelope contributes to providing a built environment with aesthetic quality as well.
 Thermal performance of building envelope is acquired a great deal of global interest. Recently, algorithms are used in architecture for generating inspired shapes from nature which could affect thermal performance. The research investigates an architectural design Methodology based on a “Modeling–Simulation–Optimization” framework to control the thermal performance of the building envelope. The design of a parametric building envelope is optimized by biomimetic algorithms such as genetic algorithms to minimize the thermal performance.
Thermal performance of building envelope is acquired a great deal of global interest. Recently, algorithms are used in architecture for generating inspired shapes from nature which could affect thermal performance. The research investigates an architectural design Methodology based on a “Modeling–Simulation–Optimization” framework to control the thermal performance of the building envelope. The design of a parametric building envelope is optimized by biomimetic algorithms such as genetic algorithms to minimize the thermal performance.
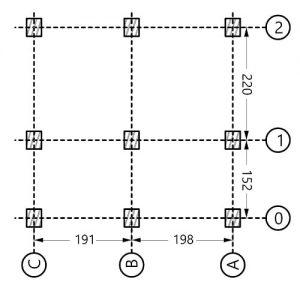
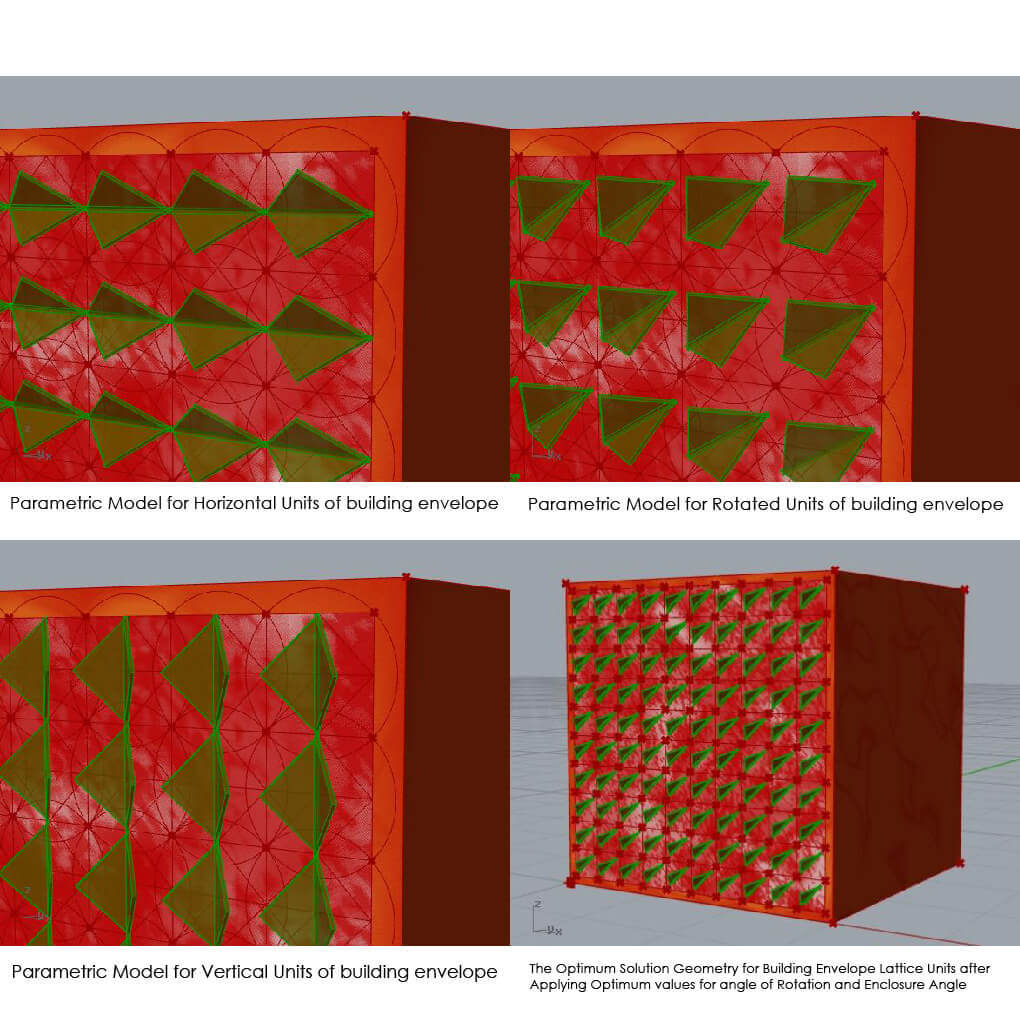 It explores the possibilities of enhancing the thermal performance of the building envelope by reducing the total thermal loads of a proposed unit in an office building. Results demonstrate that the total thermal loads for different case studies in different locations in the world are decreased when compared with the default state before the optimization process. Finally, possible configurations of the building envelope are presented to enhance thermal performance in real architectural design.
It explores the possibilities of enhancing the thermal performance of the building envelope by reducing the total thermal loads of a proposed unit in an office building. Results demonstrate that the total thermal loads for different case studies in different locations in the world are decreased when compared with the default state before the optimization process. Finally, possible configurations of the building envelope are presented to enhance thermal performance in real architectural design.











Comments