Islamic Pattern
Structural Grid Shell Design with
Islamic Pattern Topologies
Noor K. Khouri
Submitted to the Department of Architecture
in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Building Technology
at the MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
June 2017

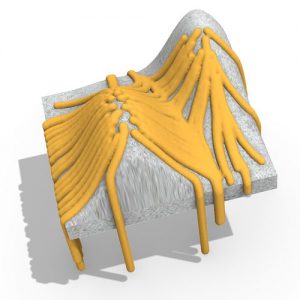
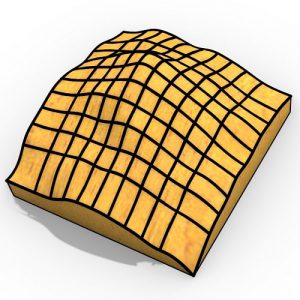
Geometric patterns, pioneered centuries ago as a dominant form of ornamentation in Islamic architecture, represent an abundant source of possible topologies and geometries that can be explored in the preliminary design of discrete structures. This diverse design space motivates the coupling between Islamic patterns and the form finding of funicular grid shells for which structural performance is highly affected by topology and geometry.
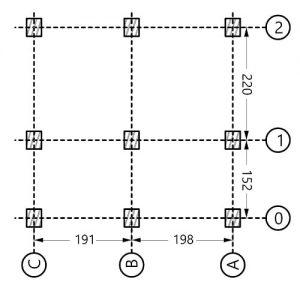
 This thesis by Noor K. Khouri, examines one such pattern through a parametric, performance-driven framework in the context of conceptual design, when many alternatives are being considered. Form finding is conducted via the force density method, which is augmented with the addition of a force density optimization loop to enable grid shell height selection.
This thesis by Noor K. Khouri, examines one such pattern through a parametric, performance-driven framework in the context of conceptual design, when many alternatives are being considered. Form finding is conducted via the force density method, which is augmented with the addition of a force density optimization loop to enable grid shell height selection.
 A further modification allows for force densities to be scaled according to the initial member lengths, introducing sensitivity to pattern geometry in the final form-found structures. The results attest to the viable synergy between architectural and structural objectives through grid shells that perform as well as, or better than, quadrilateral grid shells.
A further modification allows for force densities to be scaled according to the initial member lengths, introducing sensitivity to pattern geometry in the final form-found structures. The results attest to the viable synergy between architectural and structural objectives through grid shells that perform as well as, or better than, quadrilateral grid shells.
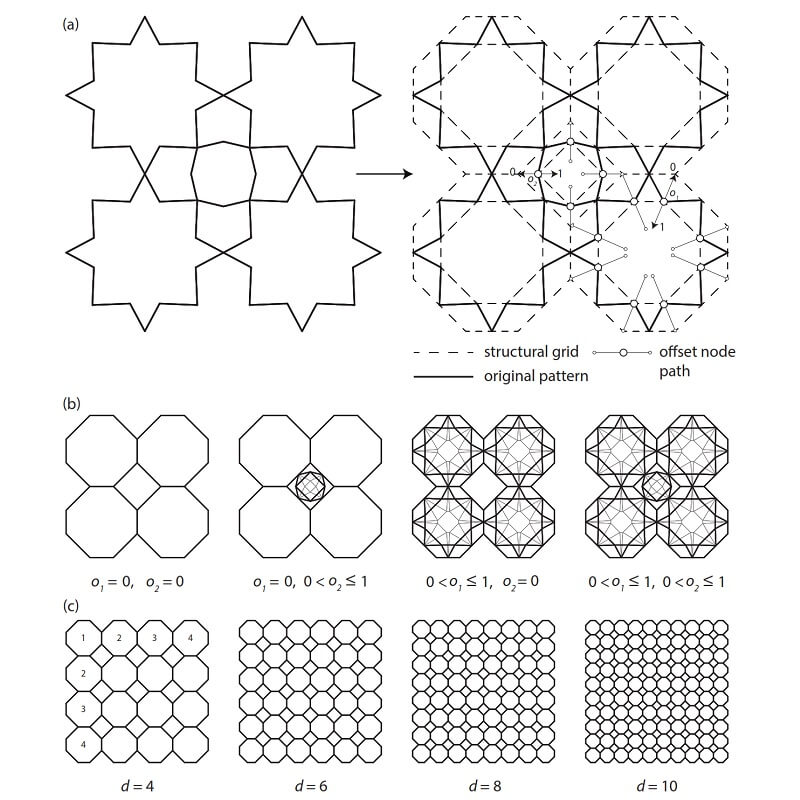 Historic and cultural patterns therefore present design opportunities that both expand the conventional grid shell design vocabulary and offer designers an alternative means of referencing vernacular traditions in the modern built environment, through a structural engineering lens.
Historic and cultural patterns therefore present design opportunities that both expand the conventional grid shell design vocabulary and offer designers an alternative means of referencing vernacular traditions in the modern built environment, through a structural engineering lens.
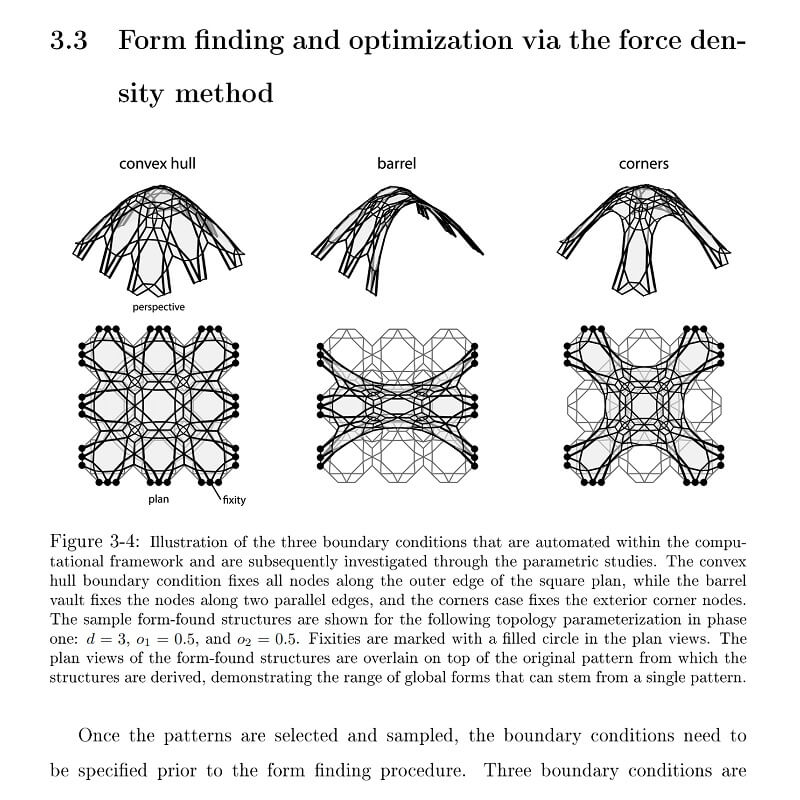
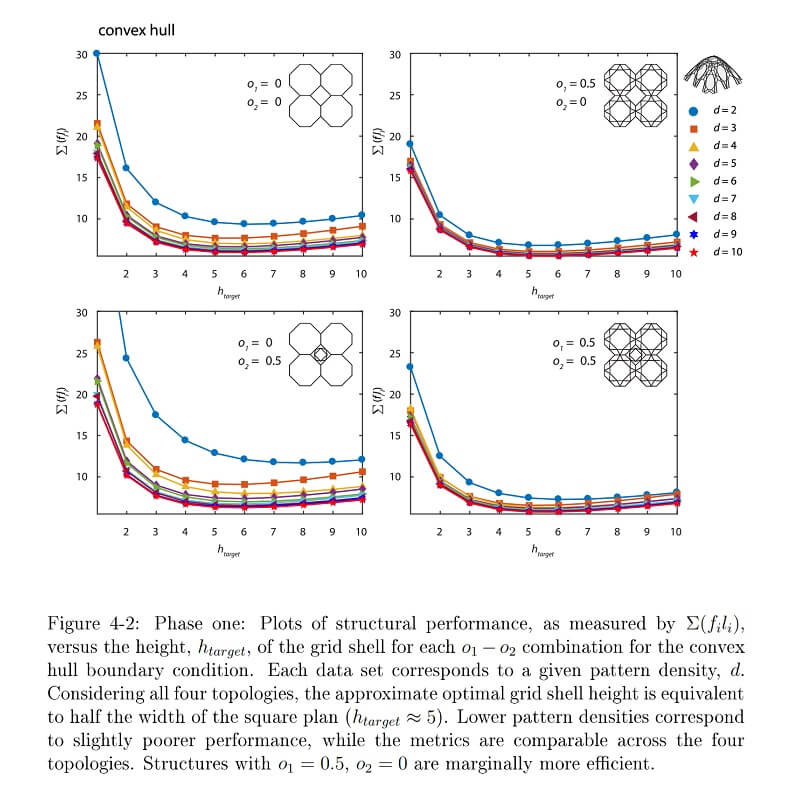
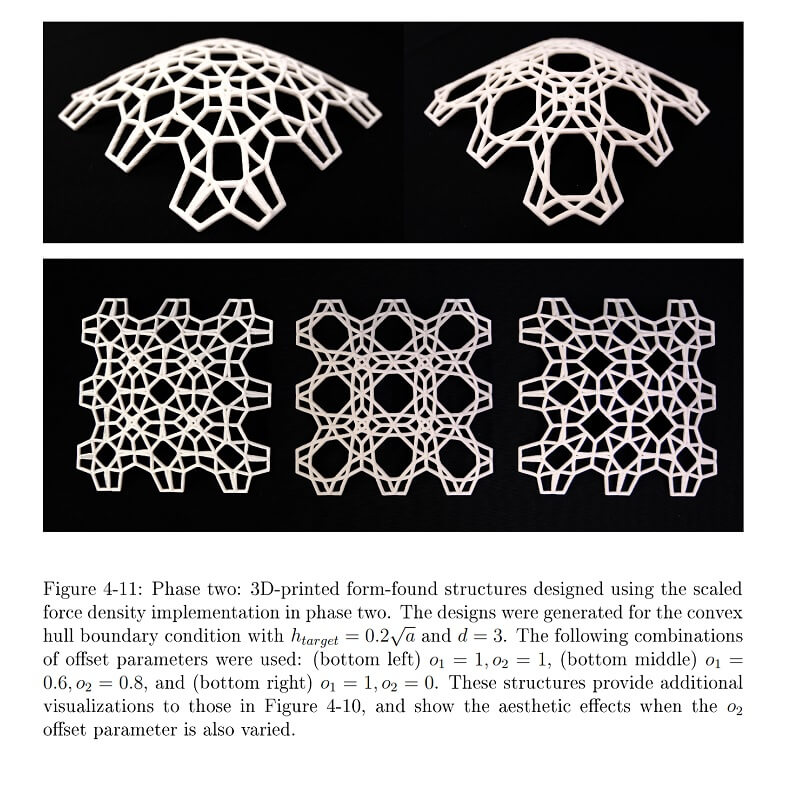













Comments